38 nematocysts discharge when
Nematocyst - Structure, Function, Types and FAQs - Vedantu When nematocysts come into contact with a crustacean prey, they discharge and pierce it, and neighboring gland cells secrete large amounts of Nv1, indicating another route for toxins to enter the body. Cnidocyte Capsule Composition: Novel Cnidaria-specific genes combine termed protein domains to form the cnidocyte capsule. How Do Jellyfish Sting? - Ocean Conservancy Nematocysts are small stinging cells that resemble tiny harpoons and are a defining characteristic of cnidarians. There are about 30 different types of nematocysts which can be used to ward off predators, secure prey and (sometimes) movement. ... The entire discharge takes about three milliseconds—faster than you can get away. Those ...
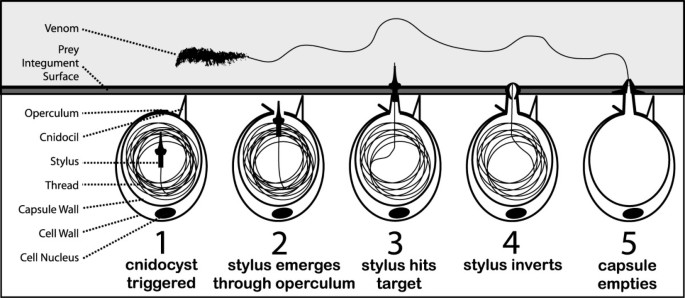
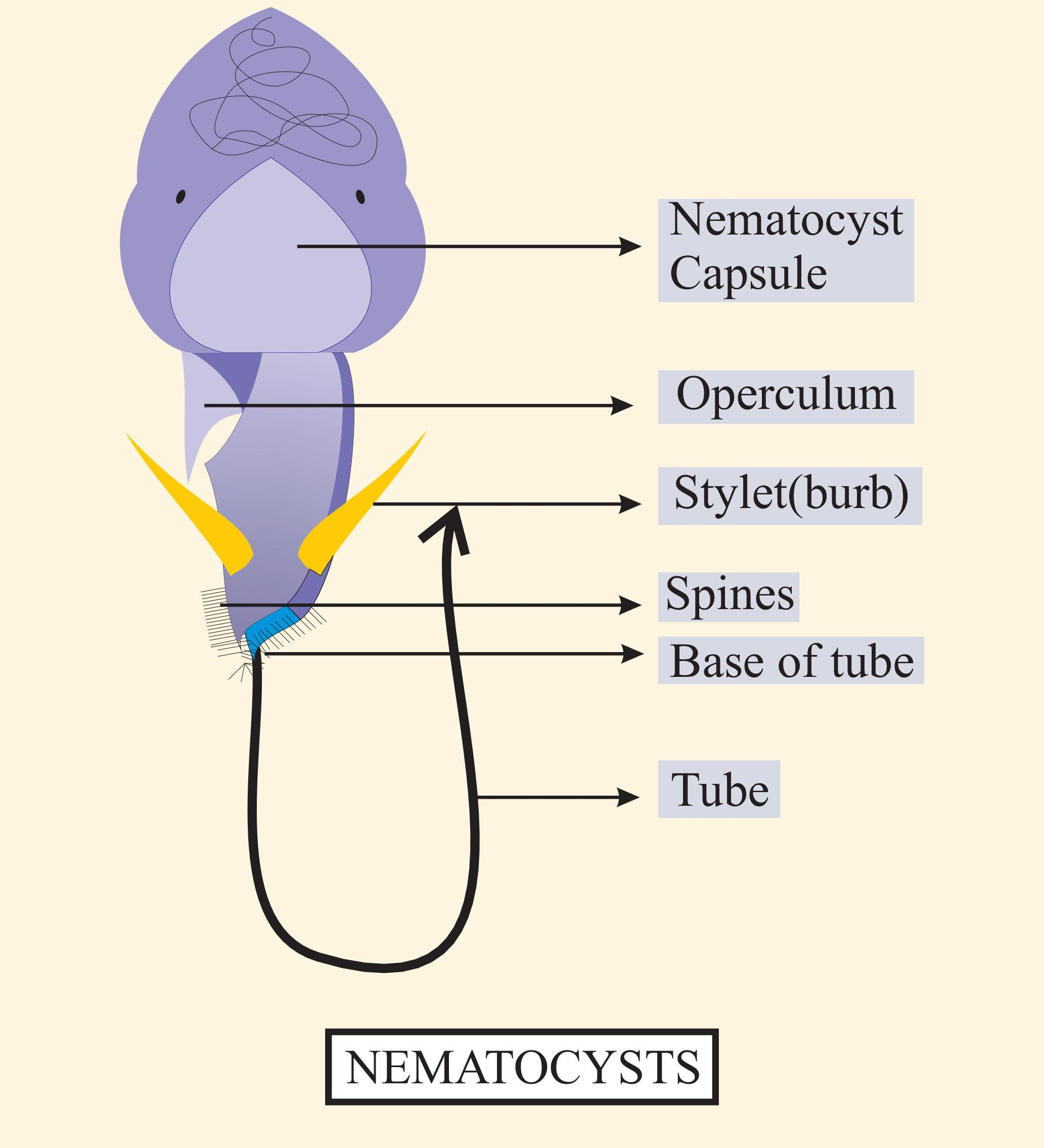
Nematocysts - The Stinging Cells | Zoology for IAS, IFoS and other ... The discharge of nematocyst thread tube from the cnidocyte takes place due to mechanical or chemical stimuli received by the cnidocil. In a resting stage the capsule wall is not permeable to water and there is very high osmotic pressure since the hypnotoxin inside is hypertonic to external water.

Nematocysts discharge when
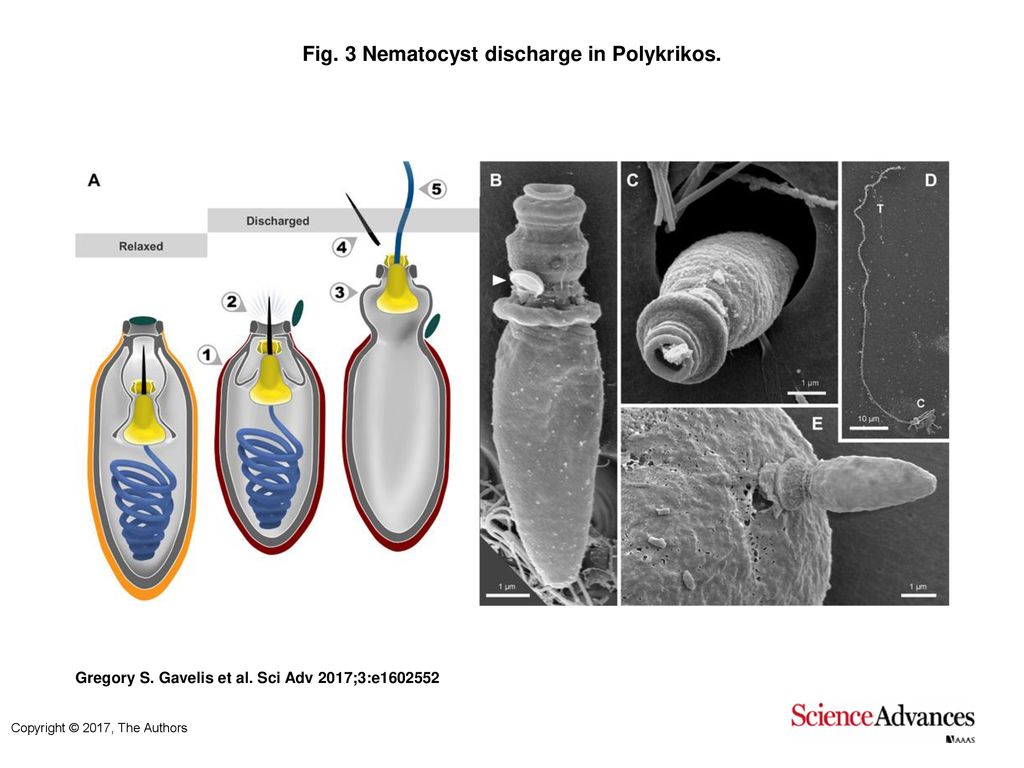
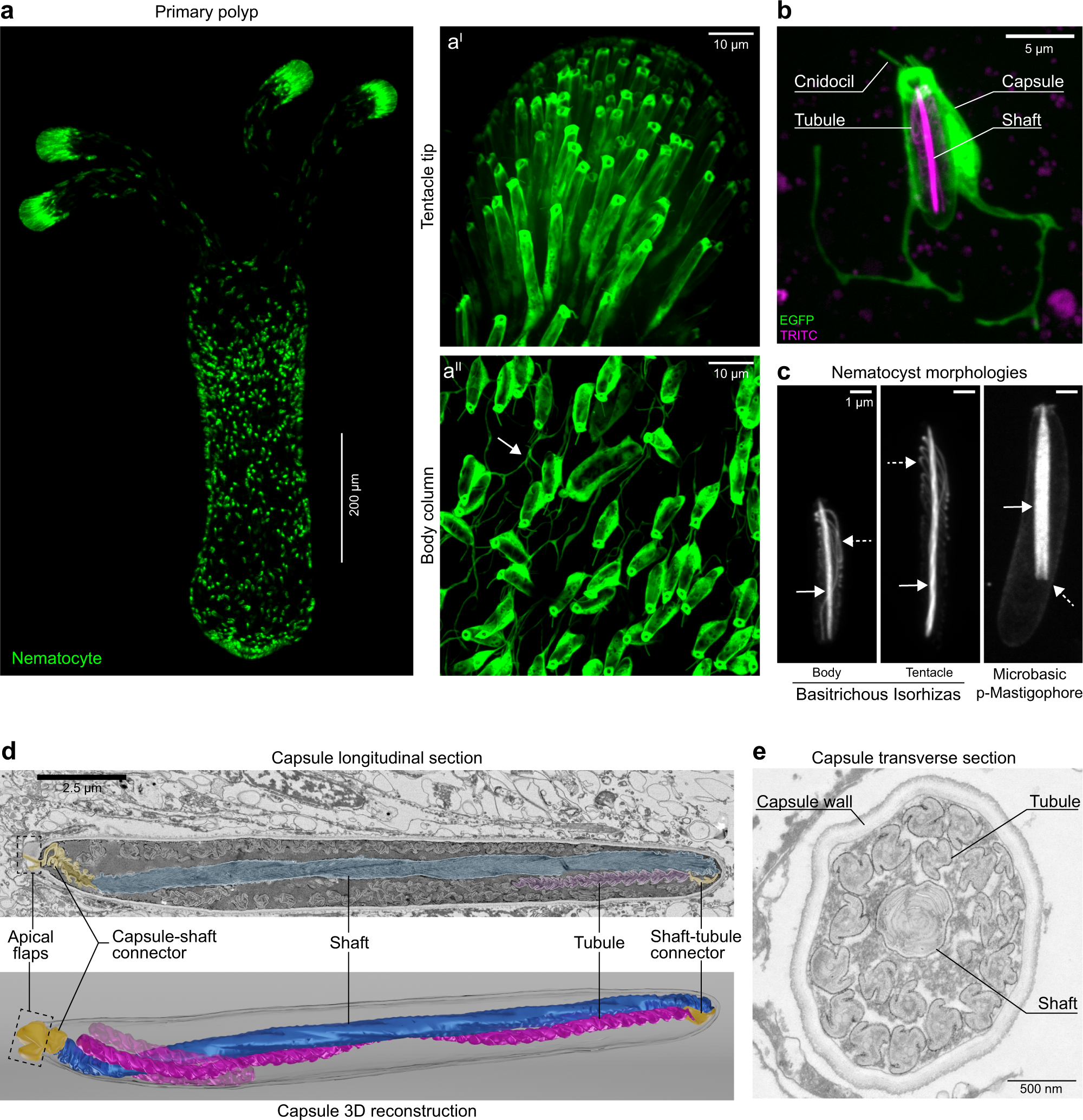
Mechanism of Nematocyst Discharge and Its Cellular Control Abstract. Cnidarians possess unique intracellular organelles, cnidae, which discharge by evaginating their tubular contents following certain appropriate stimuli. Every cnida consists of a capsule, a tubule or shaft, or combination of the two, and intracapsular fluid and is contained in a cell called a cnidocyte. Nanosecond-scale kinetics of nematocyst discharge - Cell Press The rapid discharge of stinging cells (nematocytes) in jellyfish, hydra, and other cnidarians is one of the fastest movements in the animal kingdom. After the triggering of exocytosis, a miniature cellular weapon, the nematocyst, is released and stylets punch a hole into the prey's integument. This step is so fast that conventional high-speed micro-cinematography fails to resolve its kinetics [1]. Nematocyst - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The woman was revived by rescuers and transported to a hospital where antivenom was administered; the patient was discharged after 4 days and several weeks later delivered a healthy baby. One of the rescue workers, who was also pregnant, was stung by a tentacle that was adherent on the first victim.
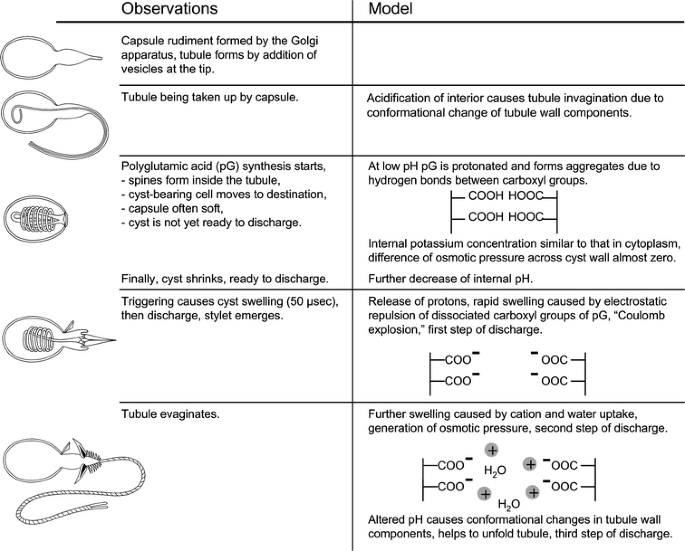
Nematocysts discharge when. Nematocyst Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary What causes nematocysts to discharge? Electrostatic repulsion, osmotic pressure generation, and conformational change at the inner tubule's surface are the three driving factors involved in nematocyst discharge, all of which come from a loss of protons. However, the influence of these several factors may change depending on the type of cyst. What Causes A Nematocyst To Discharge? - WWFAQs - World Wide FAQs Do the nematocysts discharge? Nematocysts of Hydra do not discharge when not treated with distilled water, but when transferred to saturated NaCl solution. What causes the nematocysts to fire in cnidarians? Nematocysts store a large amount of calcium ions that are deployed when the cnidocil trigger is pulled. When do Nematocysts discharge? - Answers Nematocysts are the stinging cells of cnidarians (jellyfish, corals, and sea anemones). Where are nematocysts located? Nematocysts are located within a capsule in the cell. The capsule has a... Formation and discharge of nematocysts is controlled by a proton ... Nematocysts of Hydra do not discharge when not treated with distilled water, but when transferred to saturated NaCl solution. About ten H. vulgaris were placed on the top of a FET in about 15 μl culture medium. Following the application of 10-20 μl saturated NaCl solution, the pH dropped to minimally 6.0 (Table 1 ).
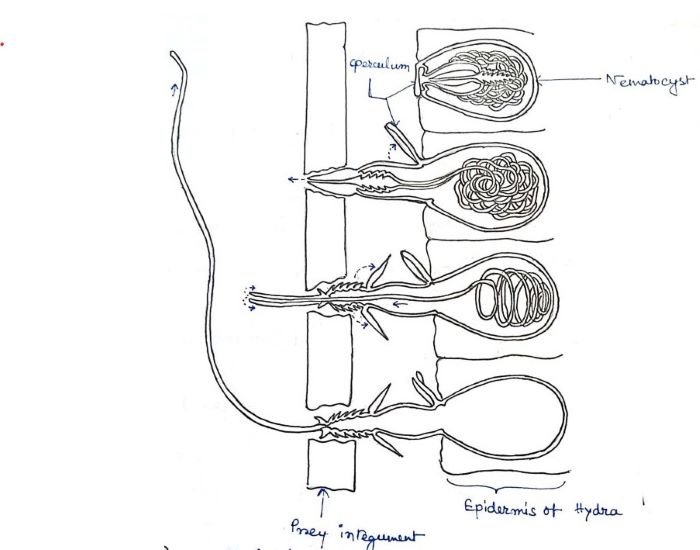
The architecture and operating mechanism of a cnidarian stinging ... At the cellular level, nematocyst discharge is among the fastest mechanical processes in nature, known to be completed within 3 milliseconds in Hydra nematocysts 11, 12. Nematocyst | biology | Britannica If a toxin is present, it passes through the hollow thread, penetrating and paralyzing the victim's tissues. After eversion, the thread separates from the nematocyst. The threads of some nematocysts ensnare small prey by wrapping about them. Nematocyst discharge in Hydra vulgaris: Differential responses of ... Locomotory nematocysts (atrichous isorhizas) discharged only in hypostome-attached tentacles contacting a substrate; desmonemes and stenoteles did not discharge during substrate attachment, implying differential neuronal inhibition. ... At higher concentrations, mucin inhibited discharge, suggesting an involvement in prey-induced feeding ... Excitation of Nematocysts | Nature If touched with a piece of human skin, there is copious discharge. The discharge, however, only takes place where there has been mechanical contact. Strong food solutions sometimes seem to...
The Cell Biology of Nematocysts - ScienceDirect The discharge of in situ nematocysts of the acontia of Aiptasia mutabilis in a Ca 2+-induced response. J. Exp. Biol., 156 (1991), pp. 173-185. CrossRef View in Scopus Google Scholar. Schultz et al., 1990. G. Schultz, W. Rosenthal, J. Hescheler. Role of G proteins in calcium channel modulation. What Causes Nematocysts To Discharge? - WWFAQs - World Wide FAQs How fast can nematocysts discharge? 700 nanoseconds. When the nematocysts are triggered they release what? The cell's thread is coiled under pressure and wrapped around a stinging barb. When potential prey makes contact with the tentacles of a polyp, the nematocyst cell is stimulated. Nematocyst - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The woman was revived by rescuers and transported to a hospital where antivenom was administered; the patient was discharged after 4 days and several weeks later delivered a healthy baby. One of the rescue workers, who was also pregnant, was stung by a tentacle that was adherent on the first victim. Nanosecond-scale kinetics of nematocyst discharge - Cell Press The rapid discharge of stinging cells (nematocytes) in jellyfish, hydra, and other cnidarians is one of the fastest movements in the animal kingdom. After the triggering of exocytosis, a miniature cellular weapon, the nematocyst, is released and stylets punch a hole into the prey's integument. This step is so fast that conventional high-speed micro-cinematography fails to resolve its kinetics [1].
Mechanism of Nematocyst Discharge and Its Cellular Control Abstract. Cnidarians possess unique intracellular organelles, cnidae, which discharge by evaginating their tubular contents following certain appropriate stimuli. Every cnida consists of a capsule, a tubule or shaft, or combination of the two, and intracapsular fluid and is contained in a cell called a cnidocyte.




























Post a Comment for "38 nematocysts discharge when"