45 diagram of syringe and needle
How To Give A Subcutaneous Injection - Drugs.com Insulin syringe: This holds a maximum of 1 mL of medicine. The syringe has markings from 10 to 100. The marking at 100 is the same as 1 mL. The marking at 50 is the same as ½ mL. Tuberculin syringe: This syringe holds up to 1 mL of medicine. It has a needle that is slightly longer than an insulin syringe. The syringe is marked every 0.1 mL. Syringe and Needle Sizes - How to choose (Guide) An insulin syringe has three parts - needle, barrel, and plunger. An insulin syringe varies in sizes from 0.25 ml to 1.0 ml. The syringe size indicates the number of units it can hold. So a 0.40 ml can hold 40 units of insulin. The larger the syringe size, the more insulin unit it can hold.
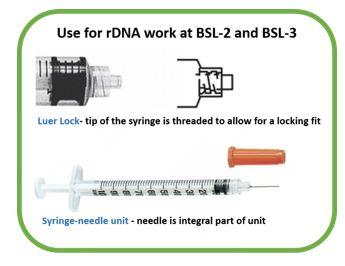
Designing a Drug-Delivery Device? Read This First Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the syringe system in which needle is pre-attached to the syringe barrel at frontend. This configuration is also called a syringe with a staked needle. The syringe barrel or container is called a primary container as it holds the medicine and has direct contact with it. The needle has two open ends and one ...
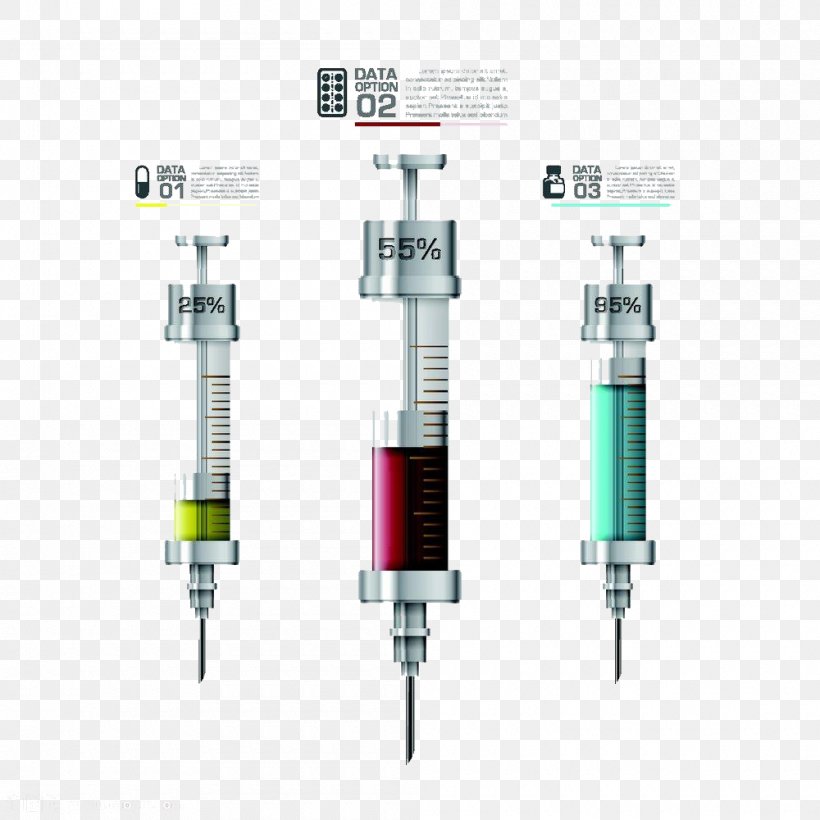
Diagram of syringe and needle
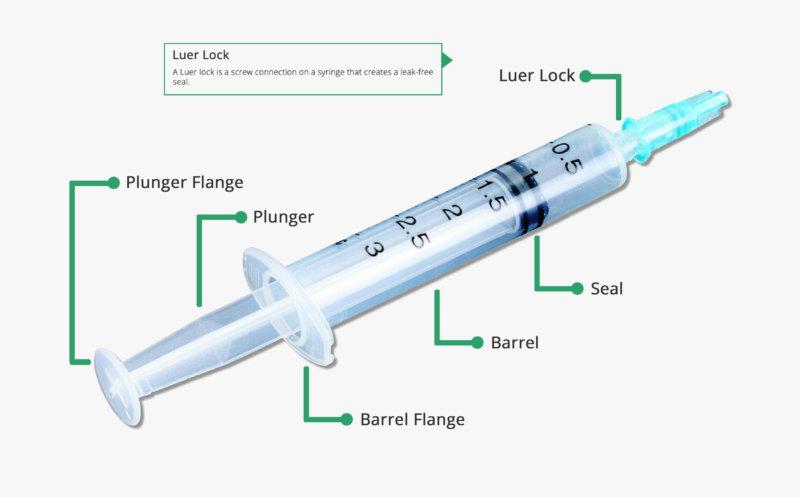
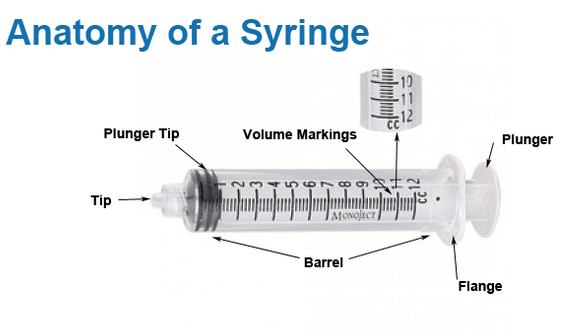
Anatomy of the Syringe • HowToDoInjections.com The anatomy of the syringe 1. Stopper Prevents leakage of medication around the plunger, and acts as an indicator for measuring the syringe's contents (see diagram). 2. Scale Markings Scale markings are typically in milliliter (mL) units. Insulin Syringe Needle Sizes Chart - DiabetesProHelp.com The recommended needle gauge ranges between 22 and 25 with a length of 5/8 inches to be introduced to the anterolateral thigh muscle. Infants 1 to 12 months The injection is introduced to the anterolateral thigh muscle with a needle gauge ranging from 22 to 25 and a needle length of 1 inch. Toddler 1 to 2 years old Expert Guide of Syringe/Needle Parts: Learn functions & diagram Syringe Parts Diagram Parts of a Syringe Plunger Thumb Rest Barrel Luer Lock Parts of a Needle Needle Hub Needle Shaft Bevel Protective Cover Syringe Parts and Functions Plunger In the Syringe, a plunger is a piston that is pressed into the barrel to force liquid through the needle.
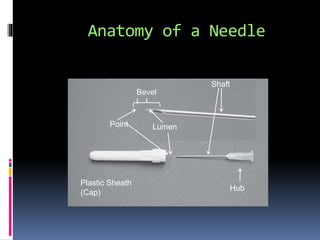
Diagram of syringe and needle. Syringe and Needle Selection Guide by Burt Cancaster Needles have a simple design with a hollow center, sharp point, and a hub that affixes to the syringe. Needle shafts come in varying lengths measured in inches. Guage sizes measure the thicknesses or diameter of the needle. Needle tips most often have a beveled tip to provide easier cutting or puncturing. How to Read Syringes: 8 Steps (with Pictures) - wikiHow Using a Syringe Accurately 1 Hold the syringe by its flange. Grasp the syringe by the winged parts located on the end of the syringe opposite from the tip. This is known as the flange. Holding the syringe this way makes it so your fingers won't be in the way while you try to read the syringe. [2] Types of Syringes & Needles | Healthfully Tuberculin syringes are used for tuberculosis testing. The fluid they contain is injected right into the skin. This syringe is small and is calibrated in milliliters. It has a long, thin barrel with a preattached needle. The tuberculin syringe can hold up to 1 ml of fluid. Even though this syringe is small, it cannot be used to give insulin. Anatomy of the Needle • HowToDoInjections.com As shown in the diagram, the thin wall needle has a narrower steel wall, allowing a greater volume of fluid to pass through it. The flow rate is typically equivalent to that of a needle one gauge larger. This is especially important with very thin needles. Extra Thin Wall
Syringe Measurements | Nurse Key Needle Gauge Diameter (thickness) of the needle shaft. The lower the gauge number, the larger the diameter of the needle. An 18-gauge needle is much larger than a 27-gauge needle. Parenteral Medications Injectable medications. Excludes oral, nasogastric, gastric, topical, and intestinal routes. PDF Vaccine Administration: Intramuscular (IM) Injection Adults 19 years of ... Use the correct syringe and needle. Administer vaccine using either a 1-mL or 3-mL syringe. Use a 22- to 25-gauge needle. Use the correct needle length based on the patient's gender and weight. For adults, use a 1- to 1.5-inch needle. in (25 mm) Men and women,Men and women, less than 60 kg* (130 lbs)60-70 kg (130-152 lbs) 1.5 in (38 mm) OR Parts of a Needle and Syringe Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Parts of a Needle and Syringe. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. How to Choose a Syringe and Needle for an Injection The needle required is small and short (typically one-half to five-eighths of an inch long) with a gauge of 25 to 30. Intramuscular injections go directly into a muscle. 4 Since muscle is deeper than the skin, the needle used for these shots has to be thicker and longer.
Different Types of Syringe's and Needles Explained Choosing the right size needle and syringe is critical in order to get the correct dose of medicine, inject it properly, and minimize the patient's pain. ... We've put together a comprehensive and detailed breakdown to help you choose the best option. Syringe Sizes Syringes are labeled based on how much liquid they can hold. There are two ways ... Parts of Syringe And Needle, Functions, Uses Syringes and needles are sterile devices used to inject substances into the body or withdraw secretions from the body. Syringes consist of a glass or plastic cylinder with a plunger at one and an opening that attaches to a needle. Syringes can be used with or without needles. For example; Syringes without needles to help with oral administration. How To Give An Intramuscular Injection (IM Injection) Open the alcohol wipe: Wipe the area where you plan to give the injection. Let the area dry. Do not touch this area until you give the injection. Prepare the needle: Hold the syringe with your writing hand and pull the cover off with your other hand. Place the syringe between your thumb and first finger. Parts of a Syringe Diagram | Quizlet Needle Definition consists of the shaft, lumen and bevel Location Term Hub Definition functions to lock the needle in place while using the syringe for its desired function Location Term Protective cap Definition maintains the needle's sterility Location Students also viewed Parts of a Syringe 10 terms DianaTRodriguez FFA officer duties 51 terms
Parts of a Syringe and Needle: Components Explained (2023) 1. Barrel. The barrel is the main body of the syringe, a transparent cylindrical chamber that holds the liquid to be injected or withdrawn. It is usually made of plastic (e.g., polypropylene) that is durable and resistant to heat and chemicals. The barrel features graduated markings that indicate the volume of the liquid inside, allowing for accurate measurement and administration of ...
Expert Guide of Syringe/Needle Parts: Learn functions & diagram Syringe Parts Diagram Parts of a Syringe Plunger Thumb Rest Barrel Luer Lock Parts of a Needle Needle Hub Needle Shaft Bevel Protective Cover Syringe Parts and Functions Plunger In the Syringe, a plunger is a piston that is pressed into the barrel to force liquid through the needle.
Insulin Syringe Needle Sizes Chart - DiabetesProHelp.com The recommended needle gauge ranges between 22 and 25 with a length of 5/8 inches to be introduced to the anterolateral thigh muscle. Infants 1 to 12 months The injection is introduced to the anterolateral thigh muscle with a needle gauge ranging from 22 to 25 and a needle length of 1 inch. Toddler 1 to 2 years old
Anatomy of the Syringe • HowToDoInjections.com The anatomy of the syringe 1. Stopper Prevents leakage of medication around the plunger, and acts as an indicator for measuring the syringe's contents (see diagram). 2. Scale Markings Scale markings are typically in milliliter (mL) units.
































Post a Comment for "45 diagram of syringe and needle"