45 label atp molecule
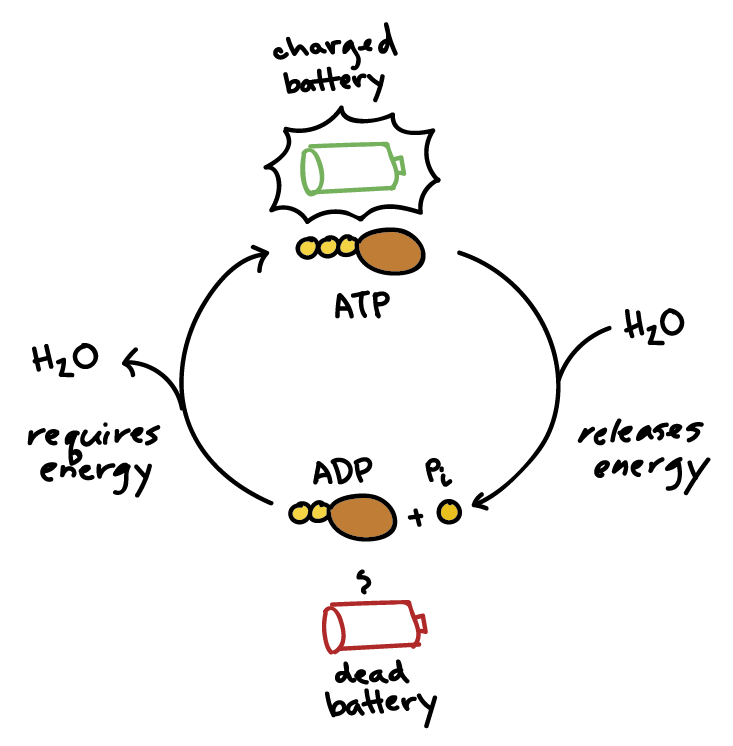
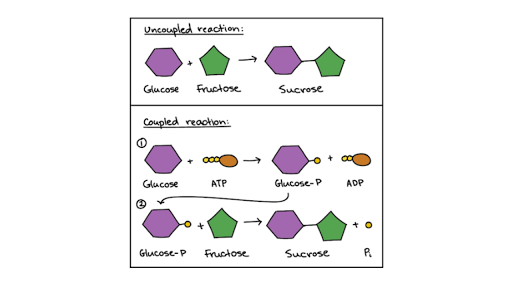
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. Photosynthesis: Crash Course Biology #8 - YouTube Hank explains the extremely complex series of reactions whereby plants feed themselves on sunlight, carbon dioxide and water, and also create some by product...
Join LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols;

Label atp molecule
› watchPhotosynthesis: Crash Course Biology #8 - YouTube Hank explains the extremely complex series of reactions whereby plants feed themselves on sunlight, carbon dioxide and water, and also create some by product... Bio Cp 1-ATP/ADP Molecules quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Three. Fill in the ATP-ADP cycle using these words...ATP, ADP, P, energy from food, energy released for cell work. ATP. Energy from food Energy released... ADP + P. Label the following diagram. Adenine (the two octagons things-FAR LEFT) Ribose (the single, darker, big Pentagon-THE MIDDLE ONE) Green fluorescent protein - Wikipedia The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label GFP traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria and is sometimes called avGFP.However, GFPs have been found in other organisms including corals, sea anemones, zoanithids, copepods …
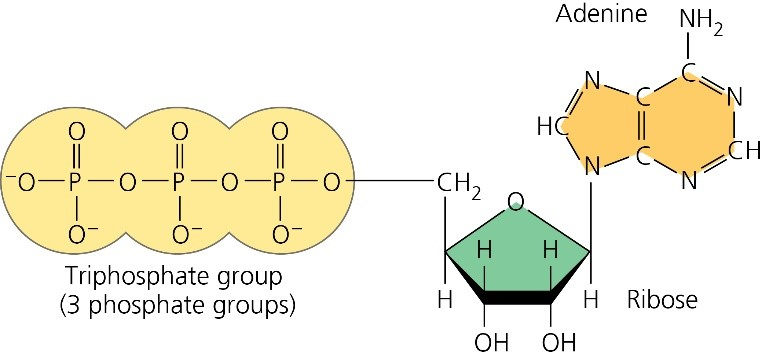
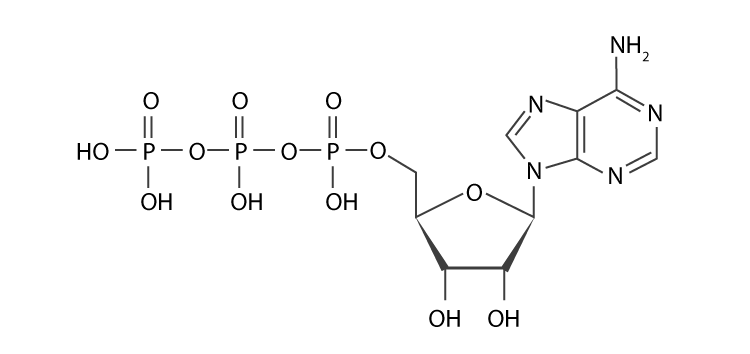
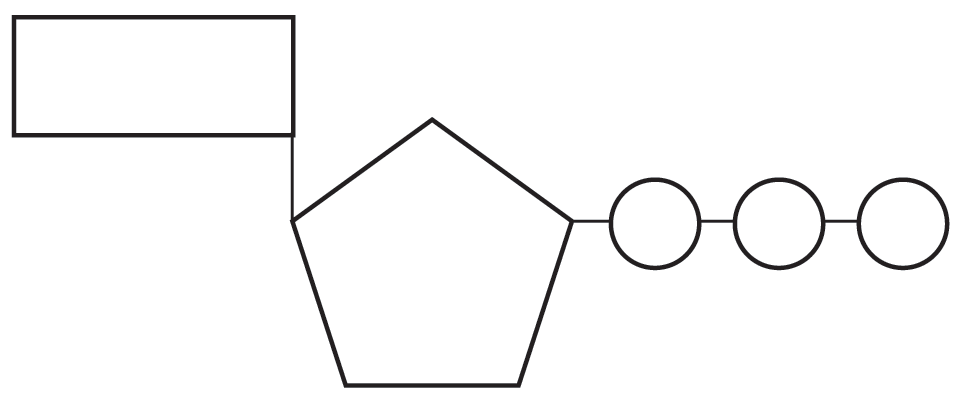
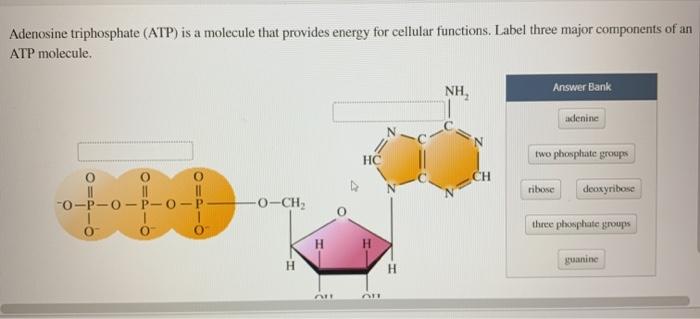
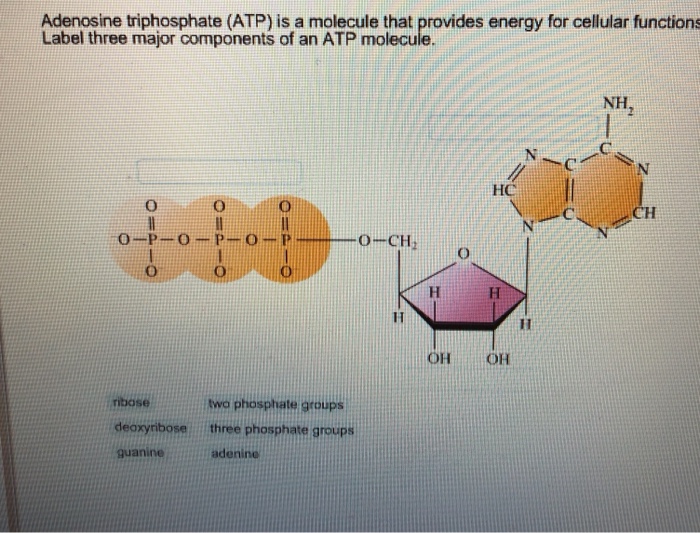
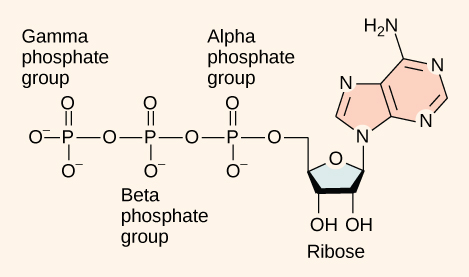
Label atp molecule. Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and... EOF Solved Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that - Chegg Question: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions Label three major components of an ATP molecule NH, C. CH OmCH FT OH OH ribose deoxyribose guanine wo phosphate groups three phosphate groups adenine This problem has been solved! Magnesium in biology - Wikipedia Magnesium is an essential element in biological systems.Magnesium occurs typically as the Mg 2+ ion. It is an essential mineral nutrient (i.e., element) for life and is present in every cell type in every organism. For example, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. . What is called ATP is often ...
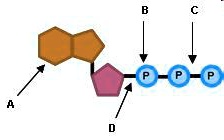
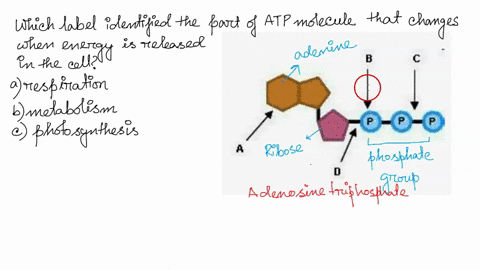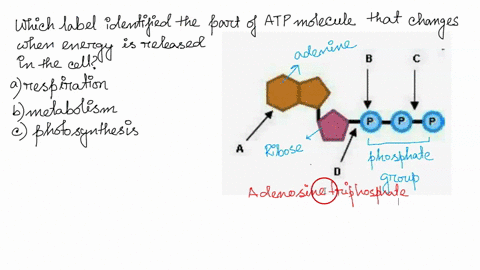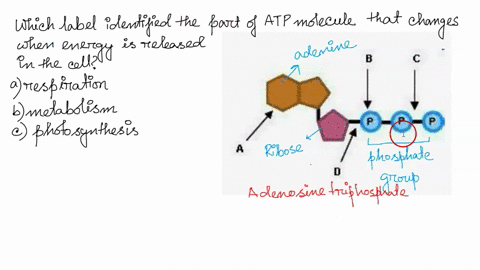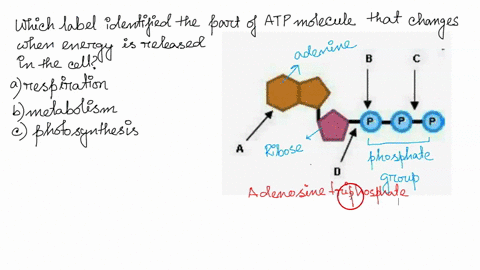
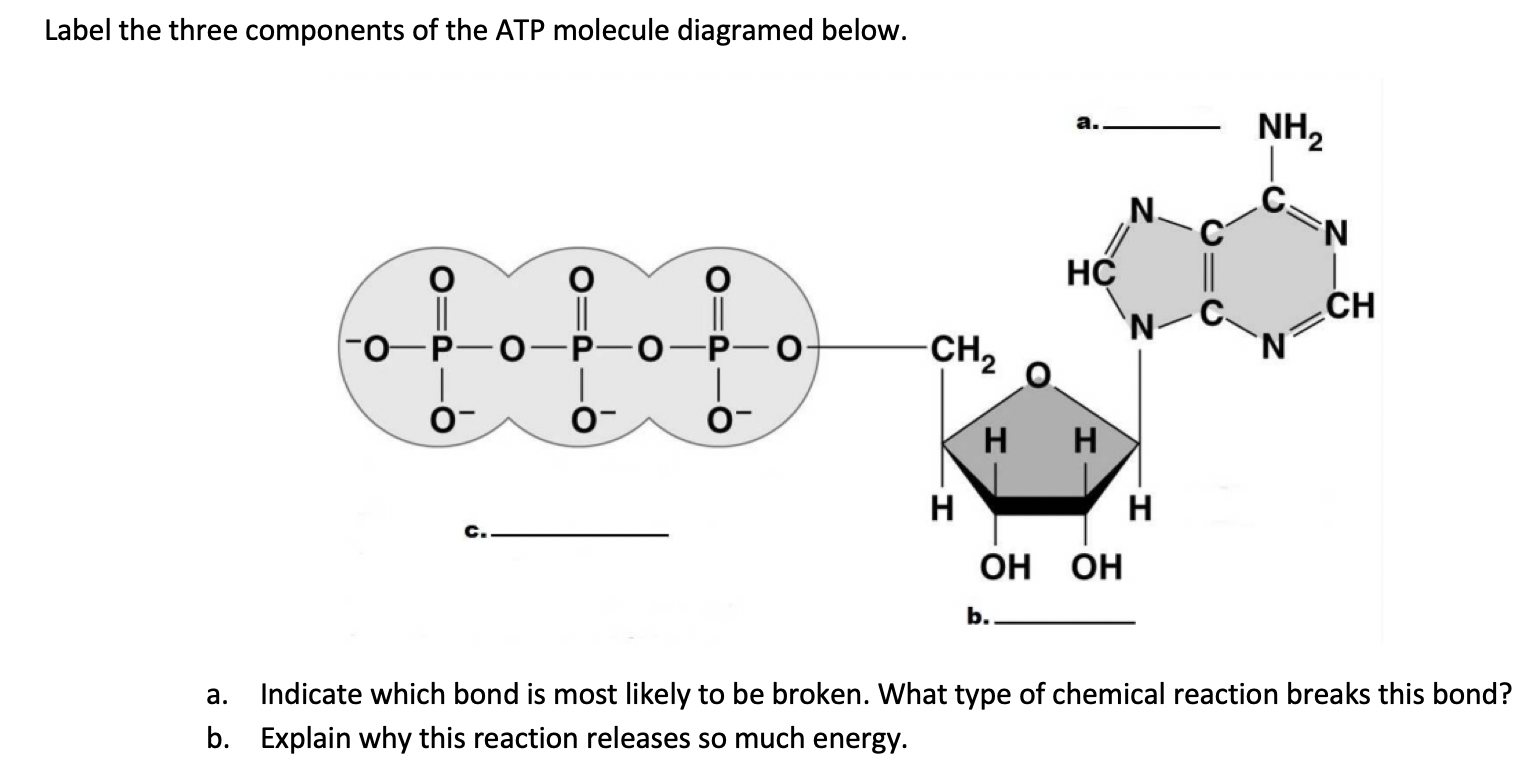
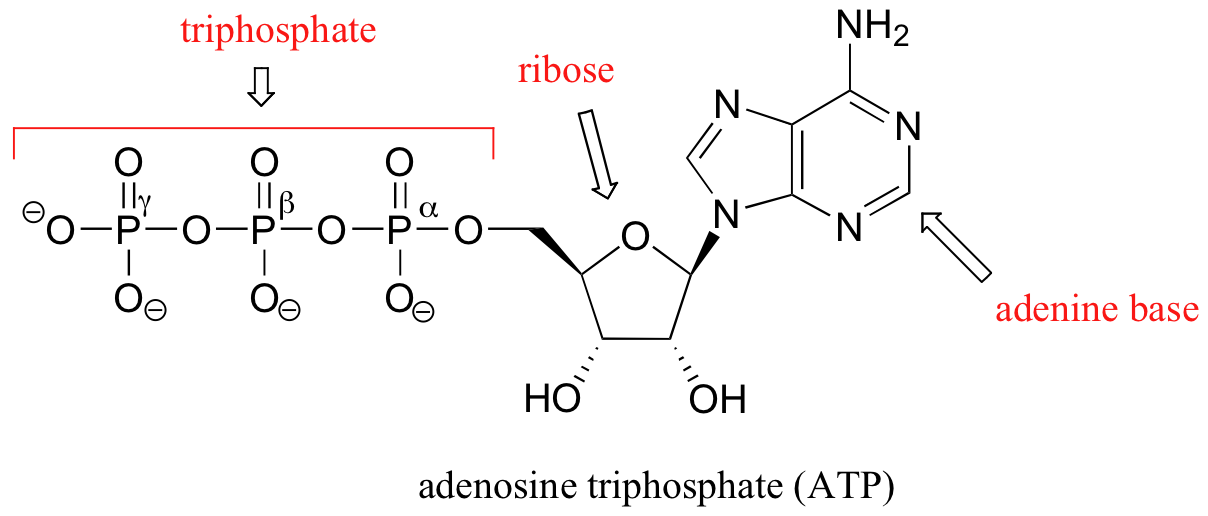
Model the Biosphere | BIOVIA – Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA solutions create an unmatched scientific management environment that can help science-based organizations create and connect biological, chemical and material innovations to improve the way we live.. The industry-leading BIOVIA portfolio integrates the diversity of science, experimental processes and information requirements, end-to-end, across research, … Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when ... Adenosine triphosphate, commonly known as ATP, is the energy carrier molecule in living cells. ATP is structurally composed of Adenine molecule (a nitrogenous base), Ribose (pentose sugar) and three phosphate groups. Energy in ATP is stored in the bonds that hold the phosphate groups together. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Green_fluorescent_proteinGreen fluorescent protein - Wikipedia The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label GFP traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria and is sometimes called avGFP. Glossary | Linus Pauling Institute | Oregon State University ATP is the molecule that is converted into ADP with a release of energy that the body then uses. ... Many biosynthetic reactions involve the addition of a one-carbon unit to a precursor molecule. Open-label trial a clinical trial in which the investigators and participants are aware of the treatment (i.e., it is not double-blind).
Solved Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that - Chegg Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. NH, Answer Bank guanine three phosphate groups v=CH deoxyribose adenine -O-P-0 - P-0 — -0-CH ribose k H H two phosphate groups ОН ОН 1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... ATP is a form of nucleotide structure which is mainly responsible for providing or driving the energy present in stored form from one point to another, through various chemical reactions. ( Metabolic pathways). It is mainly composed of three parts: A nitrogenous base, adenine, The sugar molecule, ribose. A chain of three phosphate group. Adenosine triphosphate - Wikipedia Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Light-dependent reactions - Wikipedia In chemistry, many reactions depend on the absorption of photons to provide the energy needed to overcome the activation energy barrier and hence can be labelled light-dependent. Such reactions range from the silver halide reactions used in photographic film to the creation and destruction of ozone in the upper atmosphere.This article discusses a specific subset of these, …
Chapters 5b - 7 Honors Biology Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Chapters 5b - 7 Honors Biology. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Helicase - Wikipedia The ATRX gene encodes the ATP-dependent helicase, ATRX (also known as XH2 and XNP) of the SNF2 subgroup family, that is thought to be responsible for functions such as chromatin remodeling, gene regulation, and DNA methylation. ... The other label is an organic quencher molecule. The basis of this assay is the "quenching" or repressing of the ...
ORISE Lesson Plan: Just Breathe: An Introduction to … reactants. To make a molecule of oxygen, connect two oxygen (white) atoms together. Make 6 of these and place them on the mat to the right of the yield symbol before the plus sign. 7. Sugar or glucose is a big molecule. It will take 6 carbon (pink), 12 hydrogen (green), and 6 oxygen (white). Glucose does have a specific arrangement of
Achiever Papers - We help students improve their academic standing Professional academic writers. Our global writing staff includes experienced ENL & ESL academic writers in a variety of disciplines. This lets us find the most appropriate writer for any type of assignment.
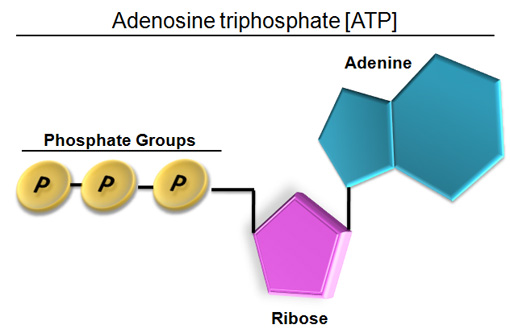
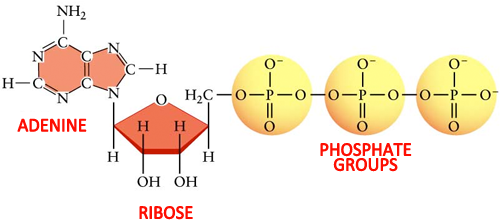
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Adenine, Ribose, and three Phosphate groups. ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture:
atp molecule labeled - davincifireplace [34] Mutations have been found throughout the ATRX protein, with over 90% of them being located in the zinc finger and helicase domains. They also play an important role in sensing viral RNAs. Label each part of the atp molecule above in the spaces provided. The other label is an organic quencher molecule. How does atp differ from adp.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › HelicaseHelicase - Wikipedia With the use of specialized mathematical equations, some of these assays can be utilized to determine how many base paired nucleotides a helicase can break per hydrolysis of 1 ATP molecule. Commercially available diagnostic kits are also available. One such kit is the "Trupoint" diagnostic assay from PerkinElmer, Inc. This assay is a time ...
orise.orau.gov › resources › k12ORISE Lesson Plan: Just Breathe: An Introduction to ... reactants. To make a molecule of oxygen, connect two oxygen (white) atoms together. Make 6 of these and place them on the mat to the right of the yield symbol before the plus sign. 7. Sugar or glucose is a big molecule. It will take 6 carbon (pink), 12 hydrogen (green), and 6 oxygen (white). Glucose does have a specific arrangement of
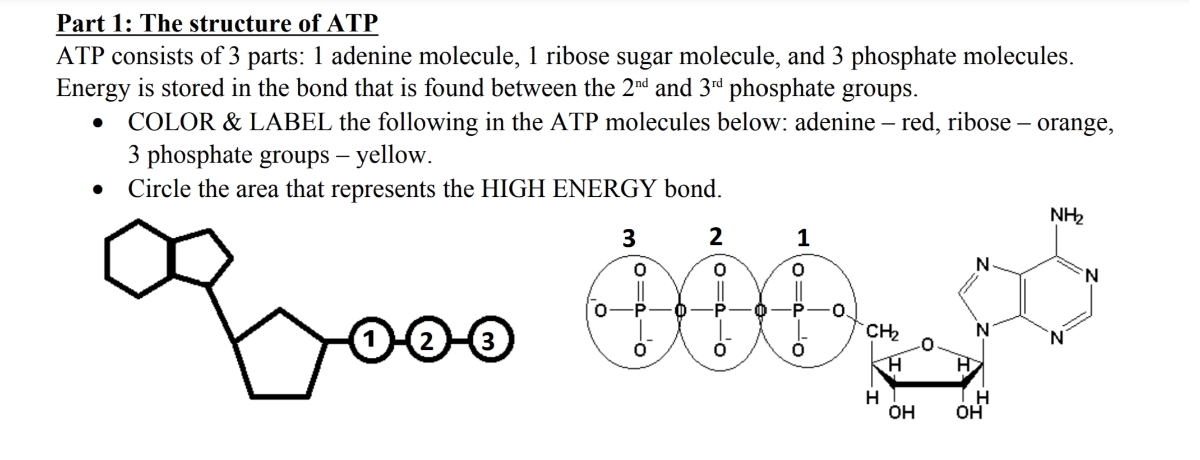
Which label identifies the part of the ATP molecule that changes when ... Answer: C; respiration. Explanation: Cellular respiration is the process by which nutrients such as glucose are broken down using oxygen to generate energy in the form of ATP, that is used to drive cellular processes.; ATP consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phosphate groups in a row. Energy from cellular respiration is stored in the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate groups ...
Label Atp Molecule - the atp molecule chemical and physical properties ... Label Atp Molecule - 16 images - 35 label each part of the atp molecule labels database 2020, photosynthesis light reactions, energy atp and adp sciencemusicvideos, simple diagram atp molecule diagramaica,
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Magnesium_in_biologyMagnesium in biology - Wikipedia For example, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main source of energy in cells, must bind to a magnesium ion in order to be biologically active. What is called ATP is often actually Mg-ATP. [5] As such, magnesium plays a role in the stability of all polyphosphate compounds in the cells, including those associated with the synthesis of DNA and RNA .
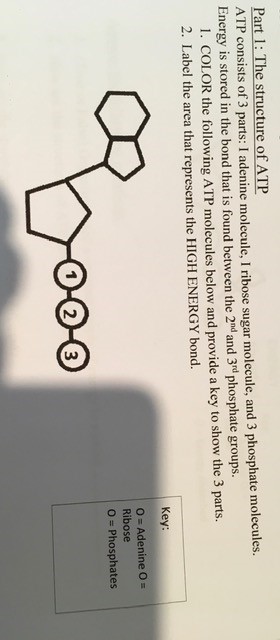
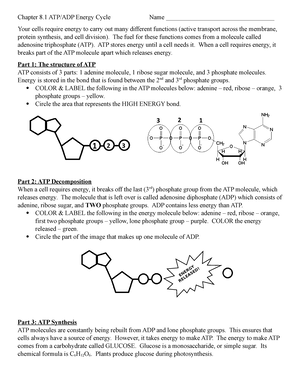
CR Study guide.pdf - 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule.... 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy (including the enzyme responsible). 2. Why is ATP important? ATP is important because it supplies energy for our cells; without it we would not have the energy to grow, move, etc. Ribose P Adenine P
› createJoin LiveJournal Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols;
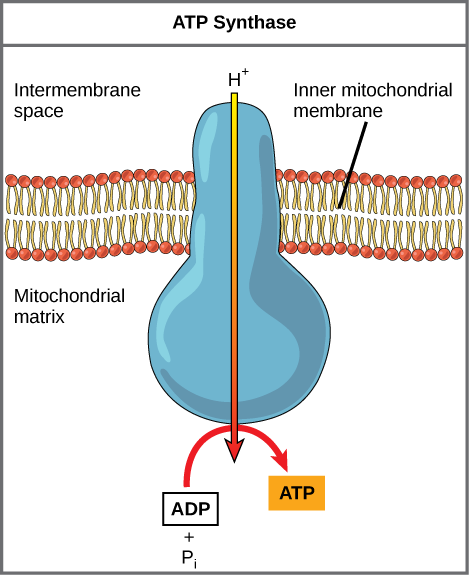
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Light-dependent_reactionsLight-dependent reactions - Wikipedia This is a cyclic process in which electrons are removed from an excited chlorophyll molecule (bacteriochlorophyll; P870), passed through an electron transport chain to a proton pump (cytochrome bc 1 complex; similar to the chloroplastic one), and then returned to the chlorophyll molecule. The result is a proton gradient that is used to make ATP ...
Green fluorescent protein - Wikipedia The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label GFP traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish Aequorea victoria and is sometimes called avGFP.However, GFPs have been found in other organisms including corals, sea anemones, zoanithids, copepods …
Bio Cp 1-ATP/ADP Molecules quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Three. Fill in the ATP-ADP cycle using these words...ATP, ADP, P, energy from food, energy released for cell work. ATP. Energy from food Energy released... ADP + P. Label the following diagram. Adenine (the two octagons things-FAR LEFT) Ribose (the single, darker, big Pentagon-THE MIDDLE ONE)
› watchPhotosynthesis: Crash Course Biology #8 - YouTube Hank explains the extremely complex series of reactions whereby plants feed themselves on sunlight, carbon dioxide and water, and also create some by product...



















Post a Comment for "45 label atp molecule"