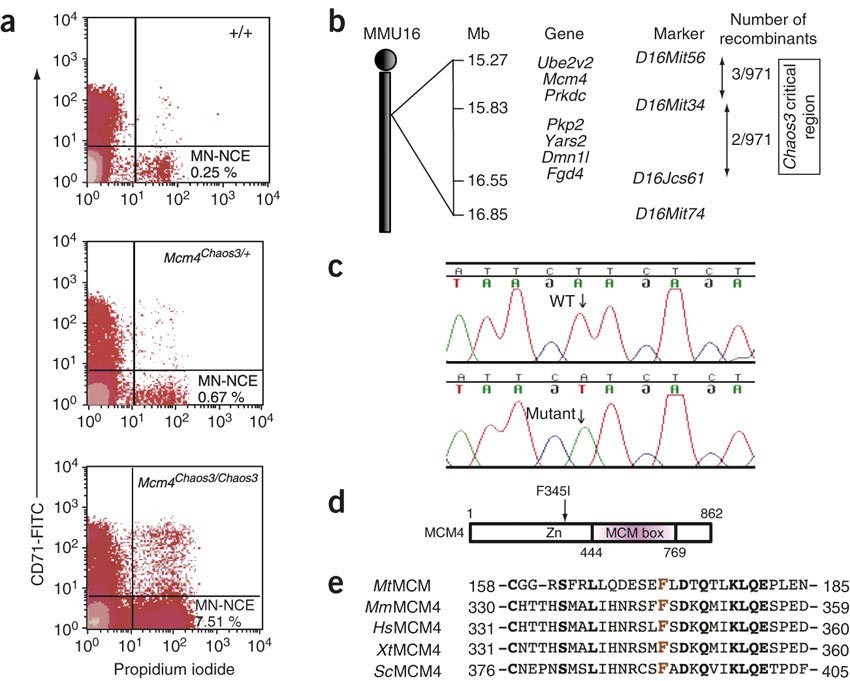
45 crossing the forked and pale mutants
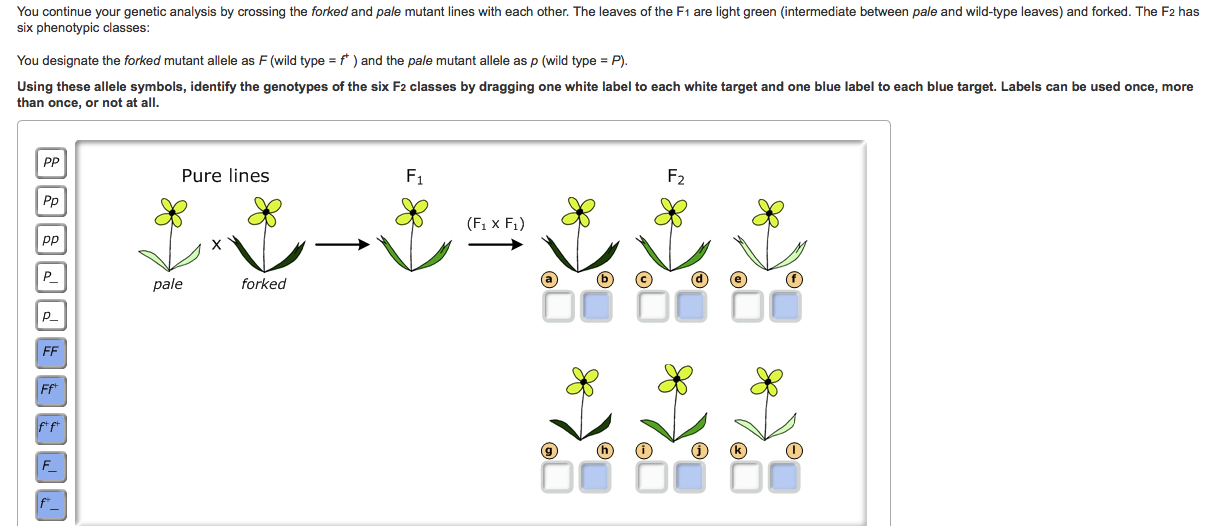
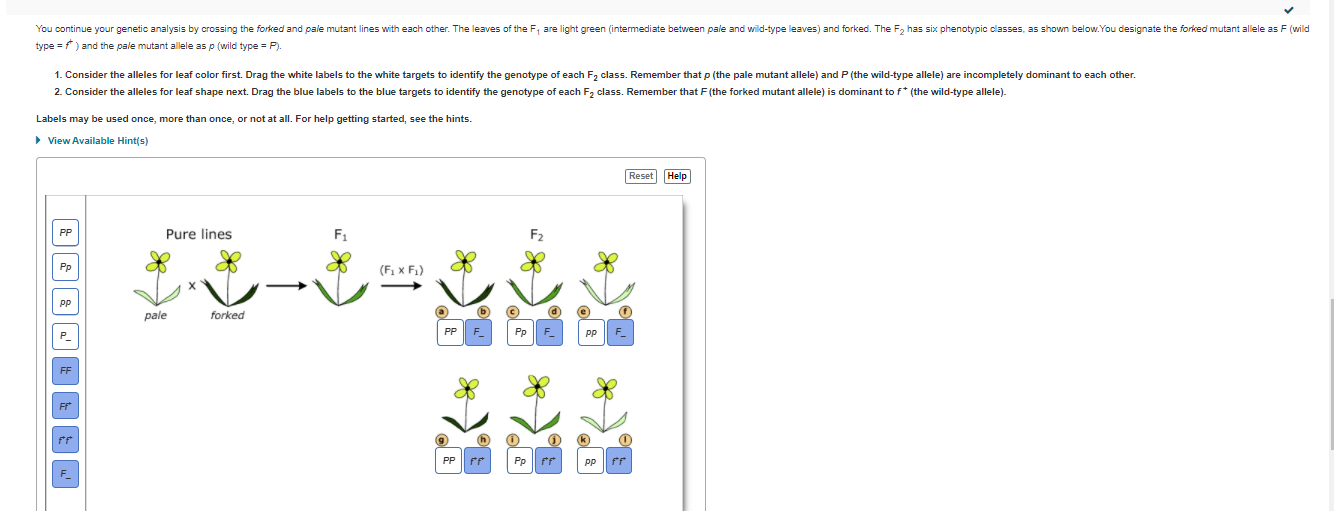
You Decide to Conduct a Genetic Analysis Part A - Determining relationships between alleles You decide to conduct a genetic analysis of these mutant lines by crossing each with a pure wild-type line. Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. Determining Relationships between alleles. PDF BIO | 201 | Principles of Biology I | homework | 4/11/2020 Ch 14 HW ... You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the . forked. and . pale. mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F ... (the pale mutant allele) and . P (the wild-type allele) are incompletely dominant to each other. ... class. Remember. that . F (the forked mutant allele) is dominant to . f + (the wild-type allele). Labels may be used ...
Bio 181 Ch. 14 HW Flashcards _ Quizlet.pdf - Upgrade Bio... View Bio 181 Ch. 14 HW Flashcards _ Quizlet.pdf from BIOLOGY 181 at RMIT Vietnam. Upgrade Bio 181 Ch. 14 HW 15 studiers in the last day Terms in this set (53) Part A - Identifying the genotype How
Crossing the forked and pale mutants
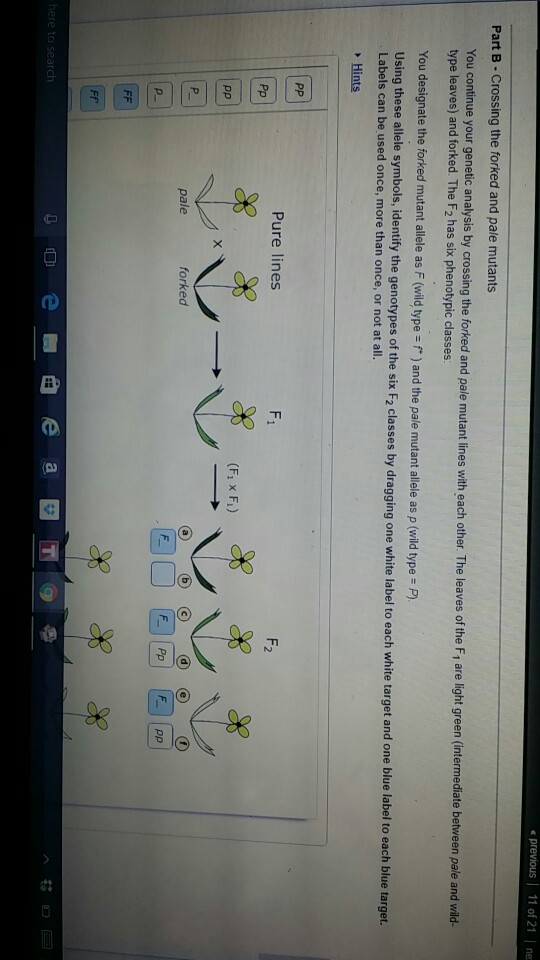
Solved: You continue your genetic analysis by cr You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes: You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+ ) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild type = P). Mastering Biology CH 14 homework Flashcards | Quizlet This cross produces four progeny types in the F1: [round, yellow], [wrinkled, yellow], [round, green], and [wrinkled, green]. Use this information to deduce the genotypes of the parent plants. Indicate the genotypes by dragging the correct label to the appropriate location. Parent genotype with yellow round: RrYy (Get Answer) - You continue your nahin by crossing the ... - Transtutors Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the Fi are light green (intermediate between pale and wild type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six... Gene Interactions You study color variants of Arabidopsis hypotheticus , a plant with red flowers.
Crossing the forked and pale mutants. Part b crossing the forked and pale mutants the green - Course Hero You designate the forkedmutant allele as F(wild type =f+) and the pale mutant allele as p(wild type =P). 1. Consider the alleles for leaf color first. Drag the white labels to the white targets to identify the genotype of each F 2class. Remember that p(the pale mutant allele) and P(the wild-type allele) are incompletely dominant to each other. 2. Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You | Chegg.com Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes, as shown below. Crossing The Forked And Pale Mutants - Blogger Crossing the forked and pale mutants. You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant . They, along side skinny pale mutants, are the only kind of mutants found in the caves. A black guinea pig crossed with an albino guinea pig produced twelve black. Pale mutants stand tall, and move in a very human like manner. Part a consider pea plants with the genotypes ggtt - Course Hero Incomplete Dominance and Codominance You are studying leaf development in a member of the mustard family. You identify several mutants of interest in this plant and make pure (true-breeding) lines of each mutant for further study. Part A - Determining relationships between alleles You decide to conduct a genetic analysis of these mutant lines by crossing each with a pure wild-type line.
Chapter 4 Flashcards | Quizlet Assume that a mutation occurs in the gene responsible for the production of hexosaminidase A, such that only about 50% of the enzyme activity is found in the heterozygote compared with a homozygous normal individual. If heterozygotes are phenotypically normal, we would say that the mutant allele is recessive to its normal allele. True Kepentingan Pendidikan Awal Kanak Kanak Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. Determining Relationships between alleles. You decide to conduct a genetic analysis of these mutant lines by crossing each with a pure-breeding wild-type line. You de Read more ... BIOL 2300 MasteringGen Ch. 4 Flashcards | Quizlet You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes: You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+ ) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild type = P). Solved You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the - Chegg You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes: You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+ ) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild type = P).
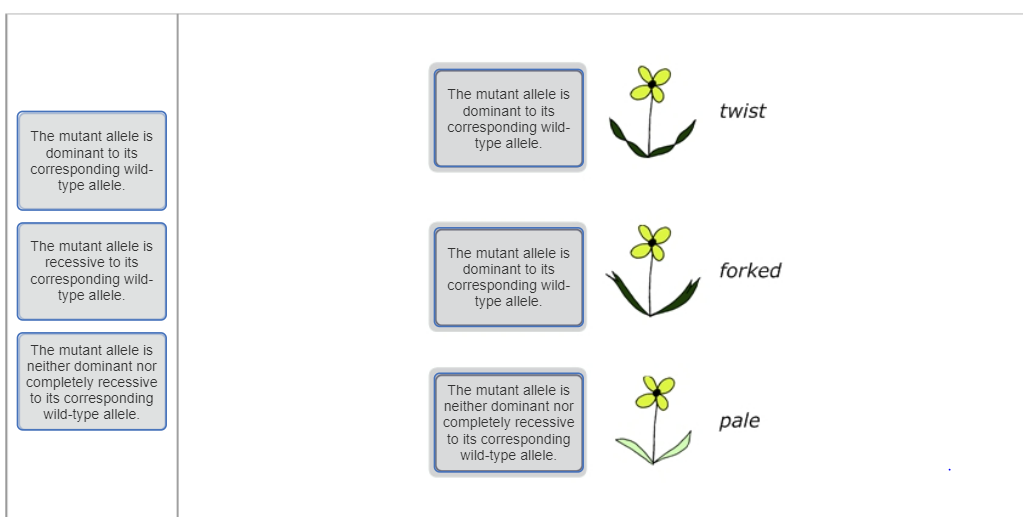
Mastering bio ch.11 Flashcards | Quizlet (Forked leaves)The mutant allele is dominant to its corresponding wild-type allele (pale leaves)The mutant allele is neither dominant nor completely recessive to its corresponding wild-type allele Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. Part b crossing the forked and pale mutants you You designate the forked mutant allele as F(wild type = f+) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild type =P). 1. Consider the alleles for leaf color first. Drag the white labels to the white targets to identify the genotype of each F 2class. Remember that p(the pale mutant allele) and P (the wild-type allele) are incompletely dominant to each other. Pengelasan Haiwan Tahun 3 - carlosghopstephens.blogspot.com Proses evolusi matematik boleh dilihat sebagai satu penambahan berterusan siri-siri pengabstrakan atau satu pengembangan isiPengabstrakan pertama yang dikongsi oleh banyak haiwan berkemungkinan adalah nombor. Doa Penerang Hati Sebelum Belajar Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. Determining Relationships between alleles. You decide to conduct a genetic analysis of these mutant lines by crossing each with a pure-breeding wild-type line. You de Read more ...
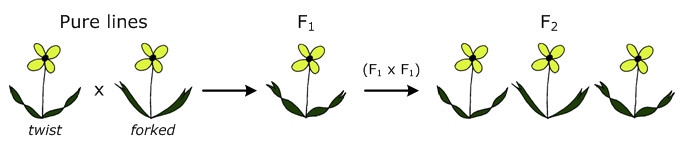
(Get Answer) - Part D - Assigning genotypes for ... - Transtutors Part D - Assigning genotypes for codominant alleles You decide to designate the twist allele as FT to distinguish it from the forked allele F. Using the following allele symbols, identify the genotypes of the three F 2 classes in Part C by dragging one label to each class. Labels may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
BIOL 2300 MasteringGen Ch. 4 - Subjecto.com Part B: Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes: You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+ ) and the ...
The Sex-Linked Group of Mutant Characters in Drosophila willistoni of crossing over between them, but not with obtaining' exact crossover values. In consequence, the " chromo- ... the color is a pale lemon, which deepens into orange as the fly matures and may become very ... this was the original appearance of the mutant and that all of the forked flies were from one mother, heterozygous for forked. Forked-2 ...
Bio 181 Ch. 14 HW Flashcards | Quizlet Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes, as shown below.
Mastering Biology Chp. 14 HW - Subjecto.com You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes, as shown below. You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+ ) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild ...
(Solved) You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and ... Solved Two lines of work indicated that crossing over actually involves breakage and re Solved An absorption line spectrum, with dark lines crossing the rainbow... Solved You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines Solved You continue your analysis by crossing the Aberdeen White and Kansas Yellow lines.
(Get Answer) - Crossing the forked and twist mutants You continue your ... Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2...
(Solved) - Part B - Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue ... Part B - Crossing the forked ...
(Get Answer) - You continue your nahin by crossing the ... - Transtutors Crossing the forked and pale mutants You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the Fi are light green (intermediate between pale and wild type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six... Gene Interactions You study color variants of Arabidopsis hypotheticus , a plant with red flowers.
Mastering Biology CH 14 homework Flashcards | Quizlet This cross produces four progeny types in the F1: [round, yellow], [wrinkled, yellow], [round, green], and [wrinkled, green]. Use this information to deduce the genotypes of the parent plants. Indicate the genotypes by dragging the correct label to the appropriate location. Parent genotype with yellow round: RrYy
Solved: You continue your genetic analysis by cr You continue your genetic analysis by crossing the forked and pale mutant lines with each other. The leaves of the F1 are light green (intermediate between pale and wild-type leaves) and forked. The F2 has six phenotypic classes: You designate the forked mutant allele as F (wild type = f+ ) and the pale mutant allele as p (wild type = P).
The effect of
























Post a Comment for "45 crossing the forked and pale mutants"