38 open-label study disadvantages
External and internal validity of open label or double-blind trials in ... In general, a blinded trial is regarded as being less subject to bias than an open trial because it minimizes the impact of knowledge of treatment allocation on post-randomized treatment decisions and on reporting of outcomes. However, a blinded trial is not always feasible. Self-Manage Scleroderma | Lesson The protocol describes what types of people may be in the trial; the schedule of procedures, tests, medications and dosages; and the length of the study. You may be eligible to participate in all or part of a research study. You will be given a complete explanation of what the study involves when you consider being a part of research trial.
The Advantages & Disadvantages of Unblinded Sample Size Re ... - Statsols The advantages of unblinded sample size re-estimation clinical trials. Earlier Decisions. You inherit the Group Sequential Design which allows the researcher to stop early for efficacy or futility. This allows the ability to adjust the trial to the reality of what the effect size is telling you will happen in the trial. Reduced Potential Cost.

Open-label study disadvantages
PDF What Are Open-Label Extension Studies For? - The Journal of Rheumatology In open-label assessment studies, there is a sig-nificant risk of biased assessment. Analysis of all subjects who were randomized (intent to treat analysis) is another important technique, since subjects who drop out can differ in crucial ways from subjects who remain in the study. In open-label extension studies, only a proportion of the sub- Open-Label Trial - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Open-label studies lack the rigor of blinded studies. Since the lack of blinding can introduce significant bias, reserve the use of open-label studies for situations in which blinding is neither feasible nor ethical or in cases where the outcome is completely objective, such as survival. Some situations include: • National Cancer Institute NCI's Dictionary of Cancer Terms provides easy-to-understand definitions for words and phrases related to cancer and medicine.
Open-label study disadvantages. Understanding Clinical Trial Terminology: What is an Open Label ... Open-label trials can be used to compare treatments or gather additional information about the long-term effects in the intended patient population. In some instances, patients who complete one clinical trial may be eligible to continue in an open-label extension study where all participants are eligible to receive active treatment for an ... PDF Blinding Sponsors for Open Label Studies: Challenges and Solutions - MWSUG the study is ongoing. The practice helps increase credibility of study results and thus should be followed, particularly for registration studies. In open label studies, in addition to treatment assignment data itself, many other data elements in the CRF data can reveal treatment assignment. Those data elements include (but not limited to): • Open-label extension studies may have legitimate place Open-label extension studies can play a legitimate, but limited, role in the clinical development of a new medicine, according to Drs Richard O Day and Kenneth M Williams of St Vincent's Hospital and Faculty of Medicine, Sydney, Australia. ... the particular advantages or disadvantages and the trends associated with open-label extension studies. PDF Labeling and Disadvantages of Labeling - University of North Carolina ... 2. Labeling enables professionals to communicate with one another because each categorical label conveys a general idea about learning characteristics. 3. The human mind requires "mental hooks" to think about problems. If present categorical labels were abolished, a new set of descriptors would evolve to take their place. There is ample evidence
Open-label extension studies: do they provide meaningful ... - PubMed Negative aspects of open-label extension studies revolve around their use as a marketing tool, as they build a market for the drug and generate pressure for subsidised access to the drug from consumers and their physicians. Open-Label Trial - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics the difference of protective efficacy of ribavirin in humans and in hamsters may have several explanations: (1) the study in humans was not randomized and performed at posteriori, and grouping treated and nontreated patients may have introduced some bias; (2) the dose and mode of infection of niv used for the challenge or the virus replication in … Reducing bias in open-label trials where blinded outcome assessment is ... This can be an issue in trials assessing surgical interventions, device trials, or other non-pharmacologic interventions, which are more difficult to blind than traditional drug trials [ 4 ]. Many such trials are therefore open-label, where patients, clinicians, and care providers are aware of treatment allocations. Cardiovascular clinical trials in Japan and controversies ... - Nature Table 1 Advantages and disadvantages of the PROBE design compared with double-blinded design. ... (Jikei Heart Study): a randomised, open-label, blinded endpoint morbidity-mortality study.
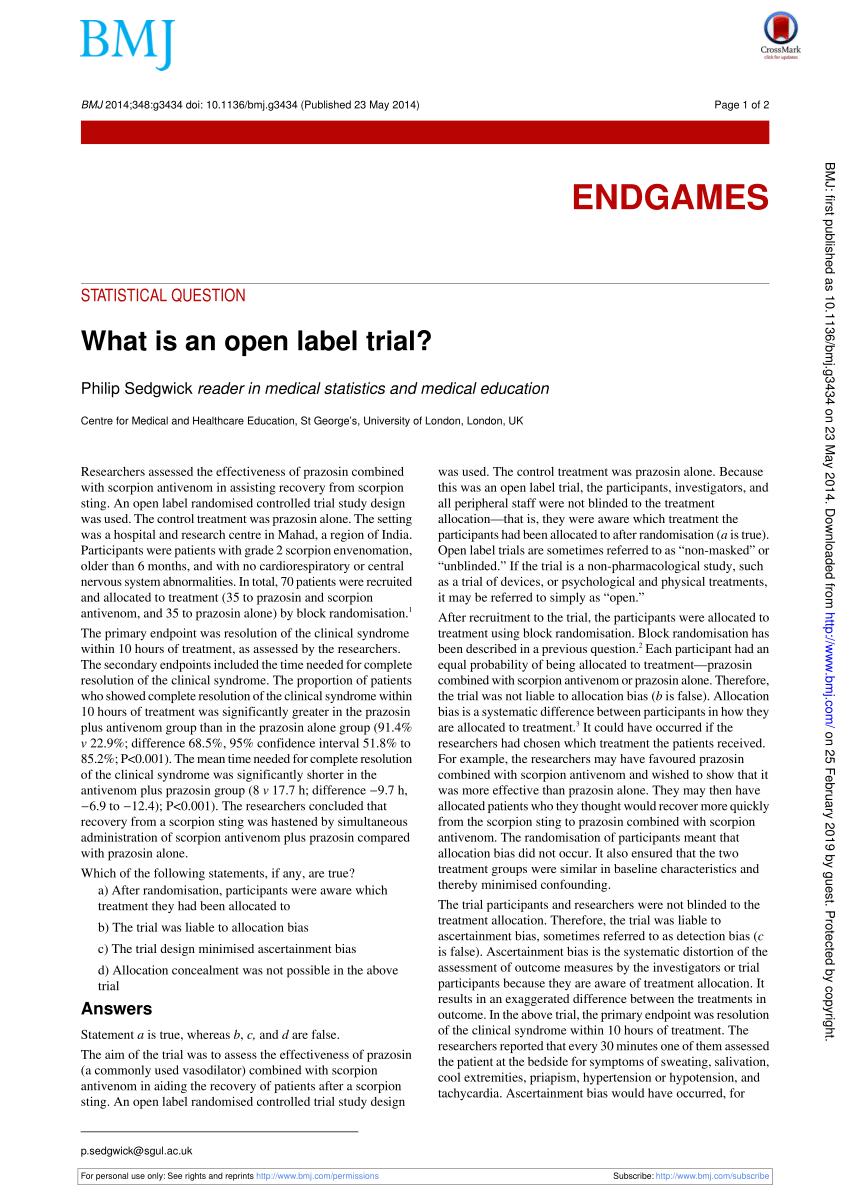
Effects of open-label placebos in clinical trials: a ... - Nature These trials assessed effects of OLPs on back pain, cancer-related fatigue, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, allergic rhinitis, major depression, irritable bowel syndrome and menopausal... Open-label study | definition of open-label study by Medical dictionary open-label study a study in which there is no blinding of treatments. Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012 open-label study A clinical study in which the patients/subjects and investigators know which product each patient/subject is receiving, which is the opposite of a blinded study. Segen's Medical Dictionary. © 2012 Farlex, Inc. Open-Label Extension Studies | SpringerLink The ethical concern that informed consent cannot be given is clear: response while receiving placebo or lack of response to the new medicine by the patient in the 'active' arm of the phase III study would not provide a sensible basis for participation in an open-label extension study. What is an open label trial? | The BMJ In an open trial, ascertainment bias can also occur on behalf of the participants. Participants know their treatment allocation and, for example, might be disappointed if not allocated their preferred treatment, with the result that they report worse scores for the outcome measures than were experienced.
External and internal validity of open label or double-blind trials in ... disadvantages of open-label or double-blind trials is currently underway and interpretation oftrialresults isoften focusedon this matter. In general, a blinded trial is regarded as being less subject to bias than an open trial because it minimizes the impact of knowledge of treatment allocation on post-random-
PDF ACKNOWLEDGMENTS - National Pharmaceutical Council crossover design removes between-patient variation.3 it requires fewer patients than a parallel study for an equal number of treatment comparisons, because each experimental unit (ie, patient) can be used several times.5this is an economical use of resources.3 patients can indicate preferences for one treatment versus another, because patients …
Effectiveness studies: advantages and disadvantages - PMC The most famous of effectiveness studies on antipsychotics is the CATIE study. 10 There is no doubt that the CATIE study is an important study when one considers, for example, the large sample size (N=1493 in 57 centers), the complex design with several parallel treatment arms, the 18-month duration of treatment of the first phase, inclusion of ...
Clinical Trial Designs - PMC - PubMed Central (PMC) In this design, after an initial open label period (enrichment period) during which all subjects are assigned to receive intervention, the non-responders are dropped from the trial and the responders (the enriched population) are randomized to receive intervention or placebo in the second phase of the trial. ... The disadvantages of this design ...
14 Advantages and Disadvantages of a Randomized Controlled Trial - Vittana List of the Advantages of Randomized Controlled Trials. 1. Randomization prevents the deliberate manipulation of results. A randomized controlled trial works to prevent skewing or the deliberate manipulation of results by researchers or participants. Because each subject gets assigned to a specific group randomly, the removal of choice works to ...
(PDF) What is an open label trial? - ResearchGate The small sample size and the dropout rate of 40% limit the generalisability of the results, as well as increase the risk of type 2 errors (Sullivan & Feinn, 2012). Another limitation is linked to...
Open-label trial - Wikipedia Open-label trials may be appropriate for comparing two similar treatments to determine which is most effective, such as a comparison of different prescription anticoagulants or possible relief from symptoms of some disorders when a placebo is given. An open-label trial may still be randomized.
Pilot Studies: Common Uses and Misuses - NCCIH Rather than focusing on feasibility and acceptability, too often, proposed pilot studies focus on inappropriate outcomes, such as determining "preliminary efficacy." The most common misuses of pilot studies include: Attempting to assess safety/tolerability of a treatment, Seeking to provide a preliminary test of the research hypothesis, and
Open-Label Trial | NIH - HIV.gov In open-label trials, both the researchers and participants know which drug (or other intervention) is being given to participants. Skip to main content Get the latest public health information from CDC ... Double-Blind Study. Print. Print this term. Download Glossary. English Version PDF(3.13MB) Spanish Version PDF(3.16MB) CONNECT WITH US ...
What is an Open-Label Clinical Trial? - News-Medical.net Day, R.O & Williams, K.M (2007) Open-label extension studies: do they provide meaningful information on the safety of new drugs? Drug Saf. 30(2) pp. 93-105 [online] Accessed online 16 th March 2022.
National Cancer Institute NCI's Dictionary of Cancer Terms provides easy-to-understand definitions for words and phrases related to cancer and medicine.
Open-Label Trial - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Open-label studies lack the rigor of blinded studies. Since the lack of blinding can introduce significant bias, reserve the use of open-label studies for situations in which blinding is neither feasible nor ethical or in cases where the outcome is completely objective, such as survival. Some situations include: •
PDF What Are Open-Label Extension Studies For? - The Journal of Rheumatology In open-label assessment studies, there is a sig-nificant risk of biased assessment. Analysis of all subjects who were randomized (intent to treat analysis) is another important technique, since subjects who drop out can differ in crucial ways from subjects who remain in the study. In open-label extension studies, only a proportion of the sub-


![PDF] Clinical trial methodology to assess the efficacy ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/a00f5af9933a8f9c61da678199905782adf4210d/8-Table4-1.png)

















![PDF] The Clinical Viewpoint: Definitions, Limitations of ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/0d341492d445073e64d1ccb6985e4ad763a3d1f7/2-Table1-1.png)




Post a Comment for "38 open-label study disadvantages"