38 labeling nucleotide examples
Anatomy, Bone Markings - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Nov 21, 2021 · Bone markings are invaluable to the identification of individual bones and bony pieces and aid in the understanding of functional and evolutionary anatomy. They are used by clinicians and surgeons, especially orthopedists, radiologists, forensic scientists, detectives, osteologists, and anatomists. Although the untrained eye may overlook bone markings as contours of the bone, they are not as ... DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides - PerkinElmer Overview. Radiolabeled nucleotides are commonly used for detection of specific nucleic acid sequences. They are typically incorporated enzymatically into DNA and RNA sequences for detection and analysis. Labeled nucleotides may be incorporated by a variety of methods including in vitro transcription with SP6, T3 or T7 RNA polymerase, 3' end ...
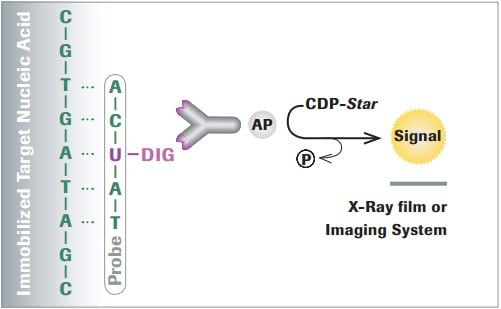
Labeling DNA Probes: Radioisotopes, Fluorophores, Biotin ... - JoVE Radioisotopes, fluorophores, or small molecule binding partners like biotin or digoxigenin, are the most widely used reporter tags for labeling DNA probes. These labels can be attached to the probe DNA molecule via end-labeling, nick-translation, or random primer synthesis methods.
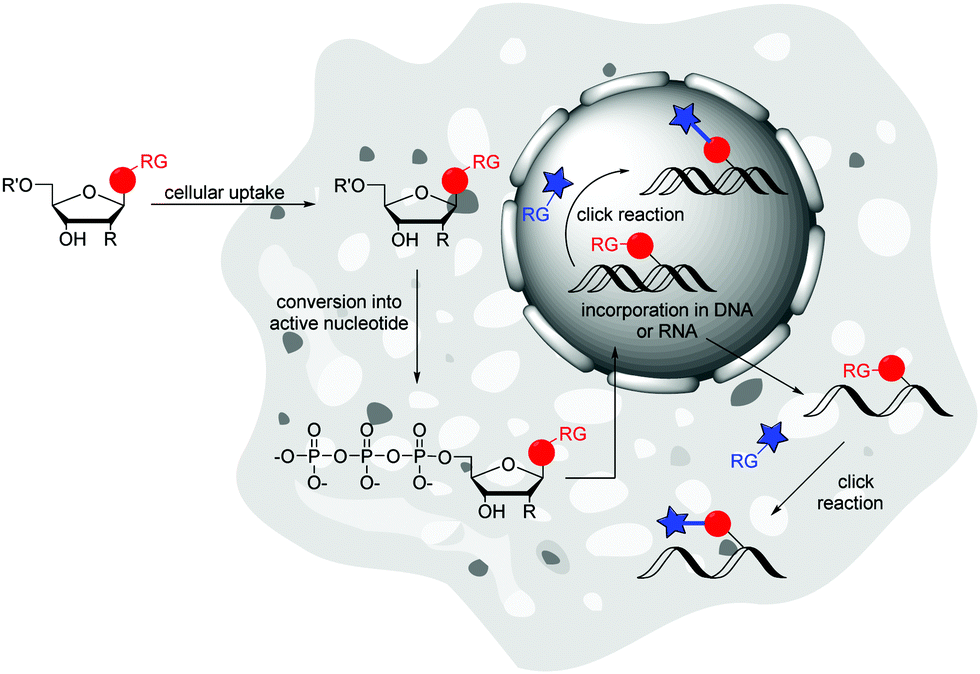
Labeling nucleotide examples
Deciphering molecular interactions by proximity labeling - Nature Jan 11, 2021 · This Review describes proximity labeling methods that make use of peroxidases (APEX) or biotin ligases (TurboID, BioID), and their applications to studying protein–protein and protein–nucleic ... New Way to Label Nucleic Acids Could Lead to New Therapies For example, nucleotides whose phosphate-backbone segments have been labeled with radioactive phosphorus are commercially available, but the phosphates in these segments can separate from the rest of the nucleotide during metabolism. To track each part of the nucleotide requires additional labeling approaches. Isotope labeling for studying RNA by solid-state NMR spectroscopy here, we discuss three different approaches towards isotope labeling of rna and their employment in ssnmr: (a) uniform and nucleotide-type selective labeling, which can be easily implemented using commercially available building blocks; (b) nucleotide-type, atom-specific labeling, which requires sophisticated methods for the synthesis of the …
Labeling nucleotide examples. Labelling of DNA and RNA in the cellular environment by ... by D Ganz · 2020 · Cited by 32 — There are rare examples of protein labellings in living cells; to the best of our knowledge, there is no published example of a Cu(I)-catalyzed ... DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides Probe labeling process radioactively label the DNA & RNA fragments for detection or purification. These Radiolabeled nucleotides are typically incorporated ... 11 Ethical, Legal, and Social Issues - NCBI Bookshelf Toxicogenomic research and its applications will raise many ethical, legal, and social issues. Because toxicogenomics involves the collection and analysis of personal genetic and phenotypic information from large numbers of individuals, it raises more significant ethical, legal and social issues than does, for example, release of reference genome sequences. Although the issues often overlap ... Nucleotides | Types, Examples, Functions & Classification Adenosine triphosphate (known as ATP) is the ideal example of a nucleotide. It contains three phosphate groups, a ribose sugar and adenine as base. It is known as the energy currency of the cell. It not only provides energy to various metabolic processes but also captures energy released in different reactions.
Simple Method for 3′-Labeling of RNA | Nucleic Acids Research | Oxford ... Two methods are commonly used for 3′-end labeling RNA: T4 RNA ligase with 3′,5′ [5′- 32 P]pCp (1,2), and poly (A) polymerase with [α- 32 P]cordycepin 5′-triphosphate (CoTP or 3′-deoxy-ATP) (3,4). Labeling with T4 RNA ligase requires high concentrations of pCp and enzyme, and is less efficient with long RNAs ( 3 ). Nucleotide - Wikipedia Examples of non-nucleic acid nucleotides cAMP, a cyclic nucleotide signaling molecule with a single phosphate linked to both 5- and 3-positions. pppGpp, a nucleotide signaling molecule with both 5'- and 3'-phosphates. NADP, a dinucleotide enzymatic cofactor . Frameshift Mutation - Definition, Examples & Effects ... Apr 28, 2017 · Radiolabeling – Also known as radioisotope labeling, is a technique used to detect the movement of a particular molecule through a chemical, biochemical or cellular system, by replacing some of the atoms in reactants with radioactive isotopes. Stop Codons – Nucleotide sequences, especially in mRNA that signal the end of translation. UAA ... dna-labeling | NEB DNA Labeling. Nucleic acids are readily labeled with tags that facilitate detection or purification. A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end ...
RNA Dynamics: Perspectives from Spin Labels Site-Directed Spin Labeling For Studying Nucleic Acids. The technique of SDSL was pioneered by the Hubble group for studying membrane proteins, and has matured as a powerful tool for studying protein structures and dynamics. 16-18 However, nucleic acids differ from proteins in their basic chemical (nucleotides vs. amino acids) and structural (A/B- helices vs. α-helix/β-strand) units. DNA Labeling - NEB A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified ... Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function Nucleotide Examples Adenine Adenine is a purine, which is one of two families of nitrogenous bases. Purines have a double-ringed structure. In DNA, adenine bonds with thymine. In RNA, adenine bonds with uracil. Adenosine triphosphate, as discussed earlier, uses the nucleotide adenine as a base. From there, three phosphate groups can be attached. Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific Common labels used to generate nucleic acid probes include radioactive phosphates, biotin, fluorophores and enzymes. In addition, the bioconjugation methods used for nucleic acid probe generation may be adapted for attaching nucleic acids to other molecules or surfaces to facilitate targeted delivery or immobilization, respectively. Page contents
Nucleotides in DNA | Science Primer DNA is a nucleotide polymer, or polynucleotide. Each nucleotide contains three components: A five carbon sugar. A phosphate molecule. A nitrogen-containing base. The sugar carbon atoms are numbered 1 to 5. The nitrogenous base attaches to base 1, and the phosphate group attaches to base 5. DNA polymers are strings of nucleotides.
The 5 Kinds of Nucleotides - ThoughtCo For example, a nucleotide that has an adenine base and three phosphate residues would be named adenosine triphosphate (ATP). If the nucleotide has two phosphates, it would be adenosine diphosphate (ADP). If there is a single phosphate, the nucleotide is adenosine monophosphate (AMP). More Than 5 Nucleotides
Nucleotide Sequence - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics A nucleic acid sequence, the messenger RNA or mRNA, is translated into the protein it encodes by means of transfer RNAs interacting with the ribosomal apparatus. Transfer RNAs bind to three nucleotides at a time and thus divide the nucleic acid sequence into triplet codons, each specifying one amino acid. However, depending on the point at ...
Fluorescent Nucleotides for RNA Labeling - Jena Bioscience RNA/cRNA Labeling Fluorescent RNA/cRNA Labeling Fluorescent Nucleotides ... Applications and selected Examples; Scientific Literature; Biosafety; IP (Licensing Information) Conference Presentations; ... 3'-RNA Labeling by… Emission color Nucleotide Cat. No. T7 RNA Polymerase T3 RNA Polymerase SP6 RNA Polymerase yPAP thT
The Order of Nucleotides in a Gene Is Revealed by DNA ... - Nature DNA is a double-stranded, helical molecule composed of nucleotides, each of which contains a phosphate group, a sugar molecule, and a nitrogenous base. Because there are four naturally occurring ...
Determination of Nucleotide Sequences | Biochemistry The ribonucleic acids which are difficult to label in vivo can be labeled in vitro (post-labeling), either at their 5′ end (after removal of the terminal 5′ phosphate, and binding of 32 P phosphate by action of a polynucleotide kinase in presence of ATP labeled on the third phosphate), or at their 3′ end (with 32 P or by periodic ...
Sanger Sequencing - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The nature of the nucleotide at a given position is now determined using specific dyes. Sanger sequencing, although too laborious and expensive for WGS, remains routinely used when sequencing of specific genes or fragment of genes is needed, for example, for viral or bacterial genotyping or for resistance testing when SNPs are associated with ...
Nucleotides labeled with... - Jena Bioscience Nucleotides labeled with... Biotin Adenosines Guanosines Uridines Cytidines Desthiobiotin Digoxigenin DNP (Dinitrophenol) Photo-labile groups ("Caged") Adenosines Guanosines Xanthosines Triple bonds (Alkyne) DBCO Azide (-N 3) Adenosines Guanosines Uridines Cytidines Thymidines TCO Vinyl Free amino group (-NH 2) Adenosines Guanosines Cytidines
Incorporation of reporter-labeled nucleotides by DNA polymerases Nucleotide analogs are routinely used to label, isolate, study, and manipulate DNA in a wide variety of applications . These nonradioactive nucleotide analogs are introduced into a DNA strand by chemical and enzymatic 5′ and 3′ end labeling and through internal enzymatic labeling or post-labeling methods . Most methods however, replace only ...
Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram | Science Trends Nucleotides are made out of elements like nitrogen and carbon with a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar component, and a group of phosphates. However, there are some important differences between RNA nucleotides and DNA nucleotides. The nitrogenous bases come in one of two different forms - they are either a pyrimidine or a purine.
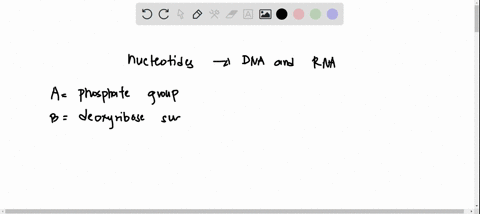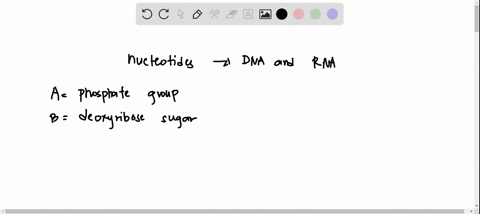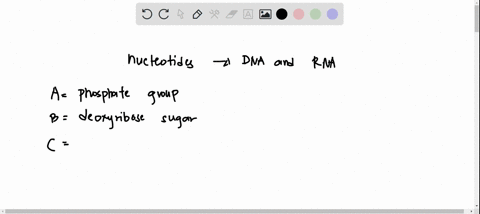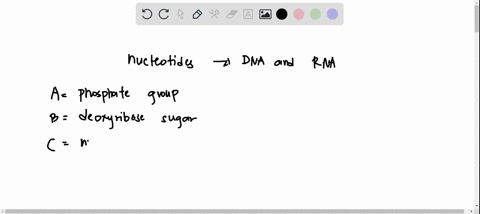
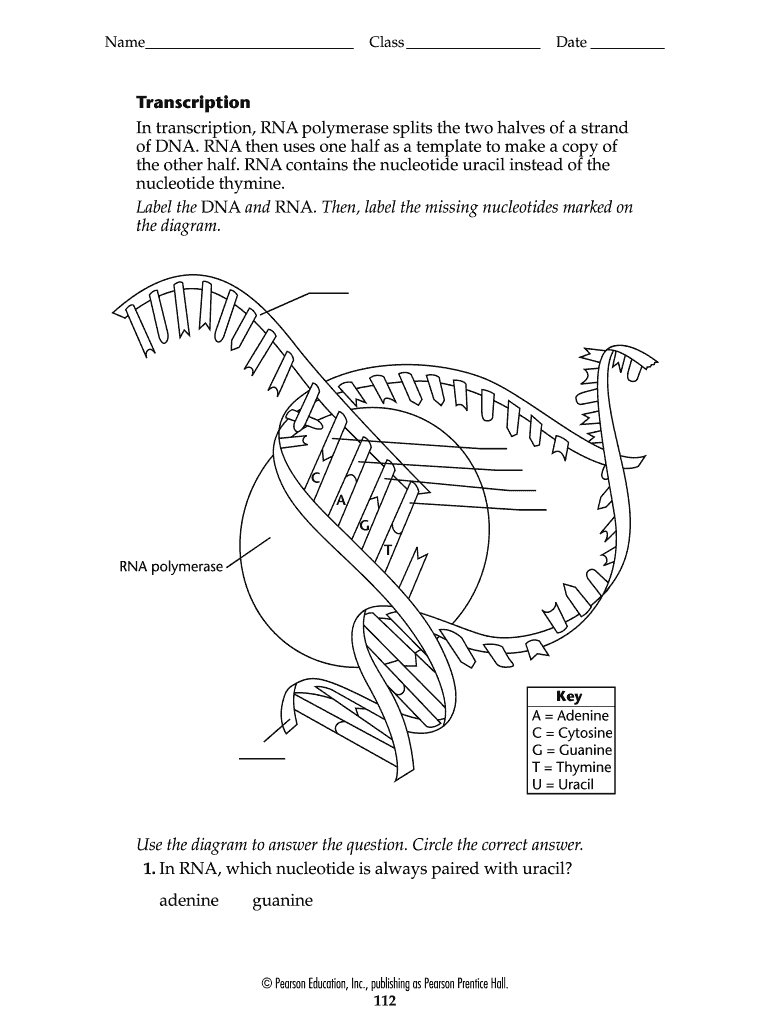
use the drop down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide label a label b label c label d label e label f 794123 roteins and nucleic acids istruction active try labeling nucleotide examples 66122
Nucleotide - Genome.gov A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
Life Science Products. Life Science Products "I just wanted to say how nice it is to do business with Life Science again. Always a #1 vendor!"-Anita (Boulder) " We love your products and your prices (and the promos are nice too) Thank you for all of the great service and help that you and your family have provided over the years – I have really appreciated working with you!
How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Explanation: The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group. 5-carbon sugar, and. nitrogenous base.
How (and Why) to Label Nucleic Acids - Bitesize Bio Mar 27, 2019 — Radioisotope labeling: Considered as a conventional method for nucleic acid labeling, radiolabeled nucleotides are synthesized using ATP-gamma- ...
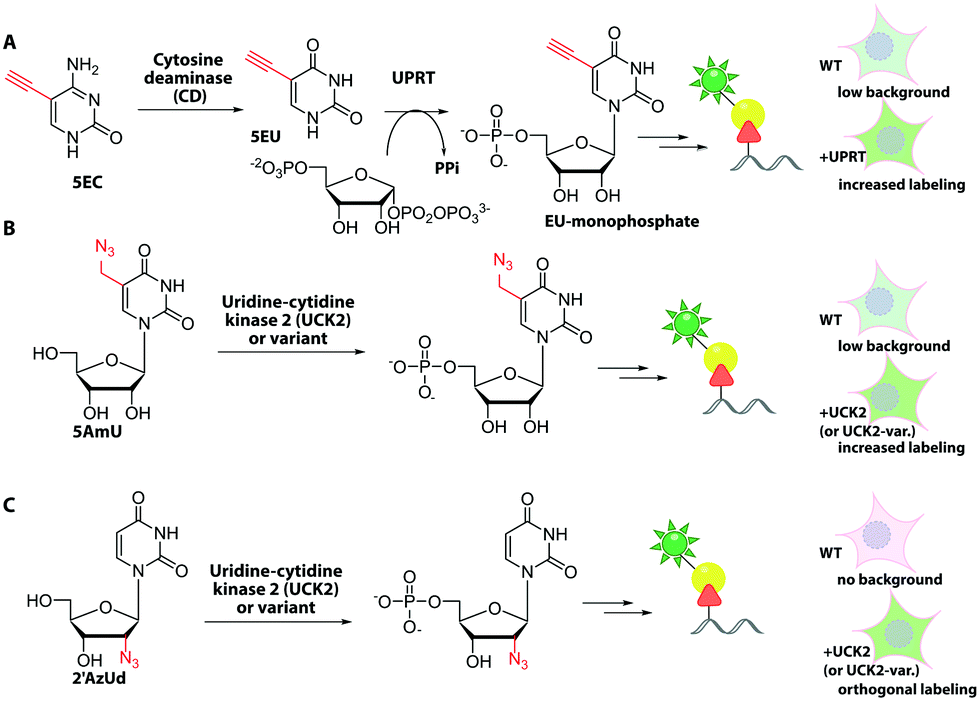
3′-End labeling of nucleic acids by a polymerase ribozyme ( A) Four different microRNAs were used as the primer for labeling by 0.1 mM 5-propargylamino-dCTP-rhodamine-12 ( 6 ), 0.05 mM 5-propargylamino-CTP-Cy5 ( 7 ) or 0.5 mM C8-alkyne-dCTP ( 9 ). The microRNAs were 5′-labeled with fluorescein. The reactions were sampled at 1 and 3.5 h and the products were analyzed by 15% PAGE.
Manually Labeling Clades on a Nextstrain Tree alt is the nucleotide that the site mutated to. For example if the nucleotide mutation is G9417A, then alt would be A. Note that some clades will be defined by more than one mutation. To avoid any conflicts with other clades, you should list all the mutations in the TSV file (using the same clade name, but different site information).
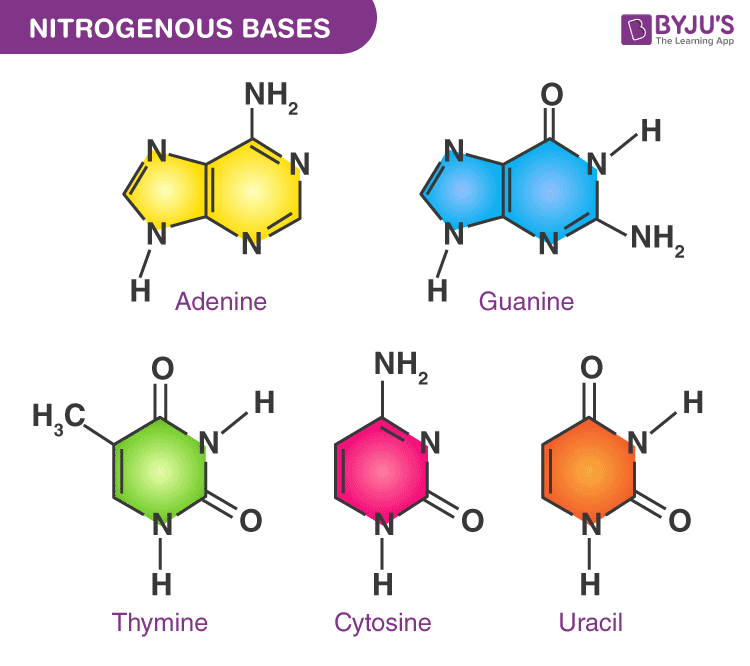
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected - ThoughtCo Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. In DNA, the bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). In RNA, the bases are adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine. Pentose Sugar In DNA, the sugar is 2'-deoxyribose. In RNA, the sugar is ribose. Both ribose and deoxyribose are 5-carbon sugars.
Nucleotide Numbering - Tulane University Nucleotide Numbering. The nucleotides are shown with standard numbering convention. The aromatic base atoms are numbered 1 through 9 for purines and 1 through 6 for pyrimidines. The ribose sugar is numbered 1' through 5'. Atoms or groups attached to the base or sugar rings atoms have the same number as the ring atom to which they are bonded.

use the drop down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide label a label b label c label d label e label f 794123 roteins and nucleic acids istruction active try labeling nucleotide examples 66122
Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 These ChromaTide nucleotides are useful for generating labeled nucleic acids for molecular biology and molecular cytogenetics applications, including chromosome and mRNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) experiments ( ), gene expression and mutation detection on arrays and microarrays ( Figure 8.2.1 ), and in situ PCR and RT-PCR.
labeling a nucleotide Diagram | Quizlet Start studying labeling a nucleotide. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Jena Bioscience RNA Labeling Selector (Kits & Nucleotides) Search Citations Search and filter all publications that cite Jena Bioscience's products by technique or by product - view publication full texts or figures and access the respective product pages!
Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS Nucleosides are named as Adenosine, Guanosine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Uridine Nucleotide = Nucleoside + Phosphate Nucleotides are named as Adenylic acid, Guanylic acid, Thymidylic acid, Cytidylic acid and Uridylic acid.
nucleotide biology Flashcards and Study Sets | Quizlet Nucleotide nucleic acids RNA A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar cov… DNA and RNA ribonucleic acid; a nucleic acid that plays an important role… 63 terms neslielopez MCAT Nucleotides - Biology Review Nucleotide pentose (sugar) Ribose a compound consisting of a nucleoside linked to a phosphate gr…
Isotope labeling for studying RNA by solid-state NMR spectroscopy here, we discuss three different approaches towards isotope labeling of rna and their employment in ssnmr: (a) uniform and nucleotide-type selective labeling, which can be easily implemented using commercially available building blocks; (b) nucleotide-type, atom-specific labeling, which requires sophisticated methods for the synthesis of the …
New Way to Label Nucleic Acids Could Lead to New Therapies For example, nucleotides whose phosphate-backbone segments have been labeled with radioactive phosphorus are commercially available, but the phosphates in these segments can separate from the rest of the nucleotide during metabolism. To track each part of the nucleotide requires additional labeling approaches.
Deciphering molecular interactions by proximity labeling - Nature Jan 11, 2021 · This Review describes proximity labeling methods that make use of peroxidases (APEX) or biotin ligases (TurboID, BioID), and their applications to studying protein–protein and protein–nucleic ...







/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)



















Post a Comment for "38 labeling nucleotide examples"