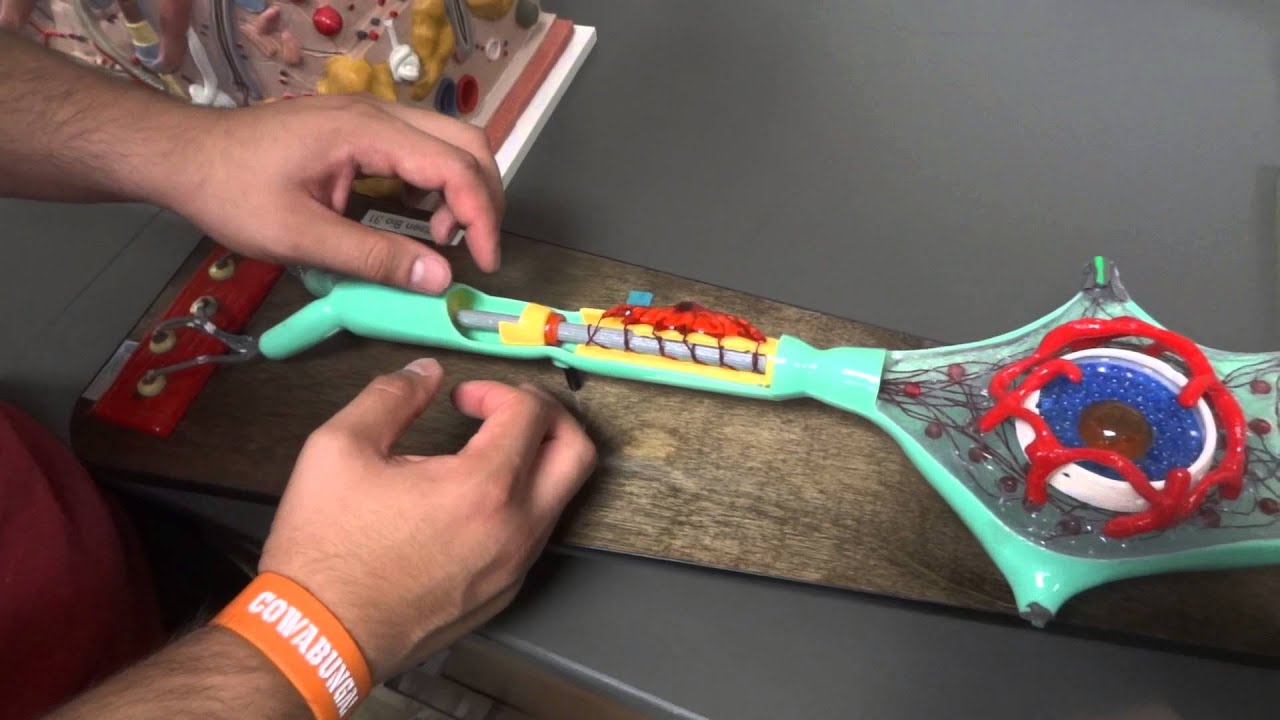
44 human cell anatomy
CELL ANATOMY - SlideShare CELL ANATOMY 1. Cell AnAtomy by Dr.Arun nArAgunD Asst.prof. shri.j g c h s A m c ghAtAprAbhA 2. The Cell Theory The cell theory (proposed independently in 1838 and 1839) is a cornerstone of biology. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living things. Cells arise only by division of previously existing cells. Cell (biology) - Wikipedia A human cell has genetic material contained in the cell nucleus (the nuclear genome) and in the mitochondria (the mitochondrial genome). In humans, the nuclear genome is divided into 46 linear DNA molecules called chromosomes, including 22 homologous chromosome pairs and a pair of sex chromosomes. The mitochondrial genome is a circular DNA ...
Anatomy and Physiology of Human Body - BYJUS Every human being, tissues, human body parts and the organ systems are made up of cells- the fundamental unit of life. Anatomy is the science of understanding the structure and the parts of living organisms. Physiology, on the other hand, deals with the internal mechanisms and the processes that work towards sustaining life.

Human cell anatomy
Free Anatomy Quiz - The anatomy of the cell - Quiz 1 centrioles, the cytoplasm, the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulums, the golgi complex, lysosomes, microfilaments, mitochondria, the nucleolus, the nucleus, the nuclear membrane, pinocytotic vesicles, the plasma membrane, ribosomes and vacuoles. Take your knowledge of the cell further with our cell physiology quizzes : Quiz 1 --- Quiz 2 Human cell - SlideShare STRUCTURE OFTHE CELL THE CELL IS MADE UP OF THE FOLLOWING STRUCTURES 1.Cell membrane or plasma membrane 2.Nucleus 3. Cytoplasm : 1. endoplasmic reticulum 2. Mitochondria 3. Ribosomes 4. Golgi apparatus 5. Lysosomes 6. Peroxisomes 7. centrosomes 8. Cilia 9. Flagella 10. Microfilaments 11. Microtubules Human Physiology - Cell structure and function Cell, or Plasma, membrane - encloses every human cell Structure - 2 primary building blocks include protein (about 60% of the membrane) and lipid, or fat (about 40% of the membrane). The primary lipid is called phospholipid , and molecules of phospholipid form a 'phospholipid bilayer' (two layers of phospholipid molecules).
Human cell anatomy. Human Cell Diagram, Parts, Pictures, Structure and Functions Diagram of the human cell illustrating the different parts of the cell. ... It contains genes, collections of DNA, which determines every aspect of human anatomy and physiology. The DNA which is arranged into chromosomes also contains the blueprint specific for each type of cell which allows for replication of the cell. PDF Cell physiology Structure and Function Humans are multicellular organisms with various different types of cells that work together to sustain life. Other non-cellular components in the body include water, macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids), micronutrients (vitamins, minerals) and electrolytes. human body | Organs, Systems, Structure, Diagram, & Facts The cell is the basic living unit of the human body—indeed, of all organisms. The human body consists of trillions of cells, each capable of growth, metabolism, response to stimuli, and, with some exceptions, reproduction. Although there are some 200 different types of cells in the body, these can be grouped into four basic classes. Anatomy and Physiology: Parts of a Human Cell - Visible Body To learn more about cells, check out our free Human Cell eBook! Cells can be divided into four groups: somatic, gamete, germ, and stem. Somatic cells are all the cells in the body that aren't sex cells, like blood cells, neurons, and osteocytes. Gametes are sex cells that join together during sexual reproduction. Germ cells produce gametes.
anatomy of a human cell anatomy of a human cell Cell Biology Wallpaper (62+ images) we have 9 Pictures about Cell Biology Wallpaper (62+ images) like Eukaryotic Cell Structure, Biology & Health Sciences Resources | Southwestern Illinois College and also Cell Biology Wallpaper (62+ images). Here you go: Cell Biology Wallpaper (62+ Images) getwallpapers.com biology cell Parts of a Cell: Lesson for Kids - Study.com Discover the parts of a cell, including the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, chloroplasts, vacuoles, ribosomes, nucleus, nuclear membrane, and chromosomes. Learn the functions of ... Human Body Anatomy - Structure of the Human Body & Parts The first section is called Gross Anatomy and deals with the study of structures that can be seen without a microscope. The second section deals with the study of structures that are microscopic and need to be examined under a microscope. Human Body Parts- A human body consists of a head, neck, trunk, arms, and legs. PDF Human Physiology/Cell physiology There are about 200 different kinds of specialized cells in the human body. When many identical cells are organized together it is called a tissue (such as muscle tissue, nervous tissue, etc). Various tissues organized together for a common purpose are called organs (e.g. the stomach is an organ, and so is the skin, the brain, and the uterus ...
HUMAN CELL - The Dr. Binocs Show | Best Learning Videos For Kids ... Hey, do you all know where you started from? You started from a CELL! Join Dr. Binocs as he takes you inside a Human Cell and tells you all about it. Voice o... An Introduction to Human Cell - Anatomy - Physiology Notes CELL MEMBRANE - It is the outermost (in the animal cell including human cell) and inner to the cell wall (in plant cells), a thin, transparent, elastic & semi-permeable membrane. It helps in exchange of materials between cytoplasm and extracellular fluid. CELL WALL - It is the outermost layer, present in the plant cell, bacteria & in algae. PDF Human Cell Diagram, Parts, Pictures, Structure and Functions A collection of cells that function together to perform the same activity is known as tissue. Masses of tissue work collectively to form an organ that performs specific functions in the body. Despite this structural organization, all activity boils down to the cell - a complex unit that makes life possible. Parts of the Human Cell Human Anatomy: The Cell Flashcards | Quizlet 1. maintenance of cell environment 2. facilitates contact with other cells or substances 3. receptor for chemicals 4. cell identity marker 5. linker 6. enzyme reaction site receptors recognizes specific ligand and alters cells function in some way ligand specific molecule that binds to a receptor cell identity markers
Types of cells in the human body: Histology | Kenhub Structurally, neurons have four specific regions; the cell body, dendrites, the axon and axon terminals. The cell body contains a nucleus and is responsible for synthesising neural proteins. The axon is long and thin, and protrudes from the cell body like a tail and can be myelinated or unmyelinated.
Cell Structure | SEER Training A cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and, between the two, the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct structures called organelles. Cell membrane Every cell in the body is enclosed by a cell ( Plasma) membrane.
Human body - Wikipedia The human body is the structure of a human being.It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems.They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.. It comprises a head, neck, trunk (which includes the thorax and abdomen), arms and hands, legs and feet.. The study of the human body involves anatomy, physiology, histology and ...
Human Anatomy - The Cell | Hungama Kids - YouTube Come join us, on this quest to know more about the most amazing machine ever built, i.e., the human body and find out about it's anatomy.There have been nume...
Human Anatomy: Blood - Cells, Plasma, Circulation, and More Blood is mostly liquid, with numerous cells and proteins suspended in it, making blood "thicker" than pure water. The average person has about 5 liters (more than a gallon) of blood. A liquid ...
11 Different Types of Cells in the Human Body - ThoughtCo Cells comprise tissues, tissues make up organs, organs form organ systems, and organ systems work together to create an organism and keep it alive. Each type of cell in the human body is specially equipped for its role. Cells of the digestive system, for instance, are vastly different in structure and function from cells of the skeletal system.
Study Guide for Anatomy & Physiology Cell Structure & Function Study Guide for Anatomy & Physiology Cellular Structure. All living organisms are made up of a cellular system. Cells are the smallest living units in our body. It is estimated the human body contains about 50 to 100 trillion cells. Each cell performs necessary functions to sustain life.
Introduction to the cell (video) - Khan Academy The type of cell that accounts for 90-95 percent of your skin are keratinocytes. Instead of being round and blob-like, their shape has a flake-shape than anything else, creating a mosaic of skin. They grow and divide in the basement membrane, a thin layer that separates your epidermis from your dermis.
Cell Structure & Function | SEER Training Cell Structure & Function Cells, the smallest structures capable of maintaining life and reproducing, compose all living things, from single-celled plants to multibillion-celled animals. The human body, which is made up of numerous cells, begins as a single, newly fertilized cell. Almost all human cells are microscopic in size.




Post a Comment for "44 human cell anatomy"